Merge remote-tracking branch 'c-cpp/master'
111
This commit is contained in:
commit
17c5b96478
@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ using namespace std;
|
||||
|
||||
class CElement;
|
||||
/***
|
||||
* @brief 单链表容器
|
||||
* @brief 单链表容器
|
||||
*/
|
||||
class CSingleList
|
||||
{
|
||||
@ -15,61 +15,61 @@ public:
|
||||
~CSingleList();
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief 插入..链表末尾插入
|
||||
* @return 成功返回非空指针,否则失败
|
||||
* @brief 插入..链表末尾插入
|
||||
* @return 成功返回非空指针,否则失败
|
||||
*/
|
||||
CElement* Insert(void* lpData, int iDataSize);
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief 插入..链表指定位置插入
|
||||
* @return 成功返回非空指针,否则失败
|
||||
* @brief 插入..链表指定位置插入
|
||||
* @return 成功返回非空指针,否则失败
|
||||
*/
|
||||
CElement* Insert(CElement* lpElement, void* lpData, int iDataSize);
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief 删除
|
||||
* @brief 删除
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void Delete(CElement*);
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief 链首
|
||||
* @brief 链首
|
||||
*/
|
||||
CElement* Begin();
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief 下一个元素
|
||||
* @brief 下一个元素
|
||||
*/
|
||||
CElement* Next();
|
||||
/***
|
||||
* @brief 链尾
|
||||
* @brief 链尾
|
||||
*/
|
||||
CElement* End();
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief 是否是空链表
|
||||
* @return 空返回TRUE,否则返回FALSE
|
||||
* @brief 是否是空链表
|
||||
* @return 空返回TRUE,否则返回FALSE
|
||||
*/
|
||||
bool Empty();
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief 反转
|
||||
* @brief 反转
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void Reverse();
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief 检测环
|
||||
* @return 返回TRUE时表示链表存在环,否则不存在环.
|
||||
* @brief 检测环
|
||||
* @return 返回TRUE时表示链表存在环,否则不存在环.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
bool CheckCircle();
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief 合并2个有序的链表
|
||||
* @brief 合并2个有序的链表
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void Merge(CSingleList& lst, std::function<int(void* t1, void* t2)>);
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief 删除倒数第K个结点
|
||||
* @brief 删除倒数第K个结点
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void DeleteLastKth(int k);
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief 求中间节点
|
||||
* @brief 求中间节点
|
||||
*/
|
||||
CElement* Center();
|
||||
private:
|
||||
@ -80,18 +80,18 @@ private:
|
||||
CSingleList(CSingleList const & rhs);
|
||||
CSingleList& operator= (CSingleList const& rhs);
|
||||
private:
|
||||
/**头结点*/
|
||||
/**头结点*/
|
||||
CElement* m_lpHead;
|
||||
/**哨兵*/
|
||||
/**哨兵*/
|
||||
CElement* m_lpSentinel;
|
||||
/**空结点,用于End()返回 */
|
||||
/**空结点,用于End()返回 */
|
||||
CElement* m_lpNull;
|
||||
/**当前结点. 枚举时使用. */
|
||||
/**当前结点. 枚举时使用. */
|
||||
CElement* m_lpCur;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
/***
|
||||
* @brief 单链表结点元素.
|
||||
* @brief 单链表结点元素.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
class CElement
|
||||
{
|
||||
@ -101,11 +101,11 @@ protected:
|
||||
~CElement();
|
||||
public:
|
||||
/***
|
||||
* @brief 获取数据指针
|
||||
* @brief 获取数据指针
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void* GetDataPtr();
|
||||
protected:
|
||||
/**下一个结点*/
|
||||
/**下一个结点*/
|
||||
CElement* m_lpNext;
|
||||
void* m_lpData;
|
||||
};
|
||||
@ -113,7 +113,7 @@ protected:
|
||||
|
||||
void CreateList(CSingleList& lst)
|
||||
{
|
||||
//循环插入元素到链表尾
|
||||
//循环插入元素到链表尾
|
||||
for(int i=1; i<10;i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int* p = new int();
|
||||
@ -134,15 +134,15 @@ void PrintList(CSingleList& lst)
|
||||
int main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
{
|
||||
/// 链表的基本操作,插入/枚举/删除
|
||||
/// 链表的基本操作,插入/枚举/删除
|
||||
CSingleList lst;
|
||||
CElement* lpElement = NULL;
|
||||
CreateList(lst);
|
||||
|
||||
std::cout<<"枚举链表当前的元素"<<std::endl;
|
||||
std::cout<<"枚举链表当前的元素"<<std::endl;
|
||||
PrintList(lst);
|
||||
|
||||
std::cout<<"查找指定元素,并在指定元素后面插入新元素"<<std::endl;
|
||||
std::cout<<"查找指定元素,并在指定元素后面插入新元素"<<std::endl;
|
||||
lpElement = lst.Begin();
|
||||
while(lpElement != lst.End())
|
||||
{
|
||||
@ -157,10 +157,10 @@ int main()
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
std::cout<<"枚举链表当前的元素"<<std::endl;
|
||||
std::cout<<"枚举链表当前的元素"<<std::endl;
|
||||
PrintList(lst);
|
||||
|
||||
std::cout<<"查找指定元素(数字是7的元素),并删除指定元素"<<std::endl;
|
||||
std::cout<<"查找指定元素(数字是7的元素),并删除指定元素"<<std::endl;
|
||||
lpElement = lst.Begin();
|
||||
while(lpElement != lst.End())
|
||||
{
|
||||
@ -172,52 +172,52 @@ int main()
|
||||
lpElement = lst.Next();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
std::cout<<"枚举链表当前的元素"<<std::endl;
|
||||
std::cout<<"枚举链表当前的元素"<<std::endl;
|
||||
PrintList(lst);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
std::cout<<"--------------------------"<<std::endl;
|
||||
{
|
||||
/// 链表的反转
|
||||
/// 链表的反转
|
||||
CSingleList lst;
|
||||
CElement* lpElement = NULL;
|
||||
CreateList(lst);
|
||||
std::cout<<"反转"<<std::endl;
|
||||
std::cout<<"反转"<<std::endl;
|
||||
lst.Reverse();
|
||||
PrintList(lst);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
std::cout<<"--------------------------"<<std::endl;
|
||||
{
|
||||
/// 检测环
|
||||
/// 检测环
|
||||
CSingleList lst;
|
||||
CElement* lpElement = NULL;
|
||||
CreateList(lst);
|
||||
std::cout<<"检测环"<<std::endl;
|
||||
std::cout<<"检测环"<<std::endl;
|
||||
bool bRet = lst.CheckCircle();
|
||||
if(bRet){
|
||||
std::cout<<"存在环."<<std::endl;
|
||||
std::cout<<"存在环."<<std::endl;
|
||||
}else{
|
||||
std::cout<<"不存在环."<<std::endl;
|
||||
std::cout<<"不存在环."<<std::endl;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
std::cout<<"--------------------------"<<std::endl;
|
||||
{
|
||||
/// 有序链表合并
|
||||
/// 有序链表合并
|
||||
CSingleList lst,lst2;
|
||||
CElement* lpElement = NULL;
|
||||
for(int i=1; i<10;i++)
|
||||
for(int i=1; i<30;i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int* p = new int();
|
||||
*p = i;
|
||||
if(i%2){
|
||||
if(i%4){
|
||||
lst2.Insert(p, 4);
|
||||
}else{
|
||||
lst.Insert(p, 4);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
std::cout<<"枚举链表当前的元素"<<std::endl;
|
||||
std::cout<<"枚举链表当前的元素"<<std::endl;
|
||||
PrintList(lst);
|
||||
std::cout<<"......"<<std::endl;
|
||||
PrintList(lst2);
|
||||
@ -231,31 +231,31 @@ int main()
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
});
|
||||
std::cout<<"合并之后,打印当前链表."<<std::endl;
|
||||
std::cout<<"合并之后,打印当前链表."<<std::endl;
|
||||
PrintList(lst);
|
||||
}
|
||||
std::cout<<"--------------------------"<<std::endl;
|
||||
{
|
||||
/// 删除倒数第K个结点,并查看中间节点
|
||||
/// 删除倒数第K个结点,并查看中间节点
|
||||
CSingleList lst;
|
||||
CreateList(lst);
|
||||
std::cout<<"删除倒数第0个结点"<<std::endl;
|
||||
std::cout<<"删除倒数第0个结点"<<std::endl;
|
||||
lst.DeleteLastKth(0);
|
||||
PrintList(lst);
|
||||
CElement* lpCenter = lst.Center();
|
||||
std::cout<<"中间节点:"<<*((int*)lpCenter->GetDataPtr())<<std::endl;
|
||||
std::cout<<"中间节点:"<<*((int*)lpCenter->GetDataPtr())<<std::endl;
|
||||
|
||||
std::cout<<"删除倒数第1个结点"<<std::endl;
|
||||
std::cout<<"删除倒数第1个结点"<<std::endl;
|
||||
lst.DeleteLastKth(1);
|
||||
PrintList(lst);
|
||||
lpCenter = lst.Center();
|
||||
std::cout<<"中间节点:"<<*((int*)lpCenter->GetDataPtr())<<std::endl;
|
||||
std::cout<<"中间节点:"<<*((int*)lpCenter->GetDataPtr())<<std::endl;
|
||||
|
||||
std::cout<<"删除倒数第3个结点"<<std::endl;
|
||||
std::cout<<"删除倒数第3个结点"<<std::endl;
|
||||
lst.DeleteLastKth(3);
|
||||
PrintList(lst);
|
||||
lpCenter = lst.Center();
|
||||
std::cout<<"中间节点:"<<*((int*)lpCenter->GetDataPtr())<<std::endl;
|
||||
std::cout<<"中间节点:"<<*((int*)lpCenter->GetDataPtr())<<std::endl;
|
||||
}
|
||||
std::cin.ignore();
|
||||
|
||||
@ -316,10 +316,10 @@ CElement* CSingleList::Insert(CElement* lpElement, void* lpData, int iDataSize)
|
||||
}
|
||||
void CSingleList::Insert(CElement* lpNewElement, CElement* lpCurElement, bool bBack /*= true*/)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if(bBack){//插入到指定元素的后面
|
||||
if(bBack){//插入到指定元素的后面
|
||||
lpNewElement->m_lpNext = lpCurElement->m_lpNext;
|
||||
lpCurElement->m_lpNext = lpNewElement;
|
||||
}else{//插入到指定元素的前面
|
||||
}else{//插入到指定元素的前面
|
||||
CElement* lpIter = m_lpSentinel;
|
||||
while(NULL != lpIter)
|
||||
{
|
||||
@ -443,11 +443,13 @@ bool CSingleList::CheckCircle()
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 合并的2个链表必须是有序的
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void CSingleList::Merge(CSingleList& lst, std::function<int(void* t1, void* t2)> fnCompare)
|
||||
{
|
||||
CElement* lpL1 = Begin();
|
||||
CElement* lpL2 = lst.Begin();
|
||||
CElement* lpTail = NULL;
|
||||
|
||||
if(!fnCompare)
|
||||
{
|
||||
@ -458,7 +460,26 @@ void CSingleList::Merge(CSingleList& lst, std::function<int(void* t1, void* t2)>
|
||||
{
|
||||
if(lpL1 != End())
|
||||
{
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 查找需要插入的正确位置
|
||||
*
|
||||
* 链表1,链表2; 链表1 <- 链表2, 链表2被合并到链表1中
|
||||
*
|
||||
* 如果链表1的元素小于链表2中的元素,则循环查找链表1中大于链表2中的当前元素的元素
|
||||
* 如果在链表1中找到满足上面条件的的元素位置[A]时,则把链表2中的当前元素插入到元素位置[A]的前面;
|
||||
* 如果在链表1中不存在这个位置则在链表1的末位插入元素
|
||||
*/
|
||||
iRet = fnCompare(lpL1->GetDataPtr(), lpL2->GetDataPtr());
|
||||
if(iRet < 0){
|
||||
lpL1 = Next();
|
||||
while(lpL1 != End()){
|
||||
iRet = fnCompare(lpL1->GetDataPtr(), lpL2->GetDataPtr());
|
||||
if(iRet > 0){
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
lpL1 = Next();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}else{
|
||||
iRet = -1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -468,17 +489,13 @@ void CSingleList::Merge(CSingleList& lst, std::function<int(void* t1, void* t2)>
|
||||
lpNewElement->m_lpData = lpL2->GetDataPtr();
|
||||
if(lpL1 != End())
|
||||
{
|
||||
Insert(lpNewElement,lpL1, iRet <= 0);
|
||||
Insert(lpNewElement,lpL1, iRet < 0);
|
||||
}else{
|
||||
if(NULL == lpTail)
|
||||
{
|
||||
lpTail = Tail();
|
||||
}
|
||||
CElement* lpTail = Tail();
|
||||
Insert(lpNewElement,lpTail);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
lpL2 = lst.Next();
|
||||
lpL1 = Next();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
0
c-cpp/13_sorts/.gitkeep
Normal file
0
c-cpp/13_sorts/.gitkeep
Normal file
43
c-cpp/13_sorts/bucket_sort.hpp
Normal file
43
c-cpp/13_sorts/bucket_sort.hpp
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Created by Liam Huang (Liam0205) on 2018/10/26.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef SORTS_BUCKET_SORT_HPP_
|
||||
#define SORTS_BUCKET_SORT_HPP_
|
||||
|
||||
#include <iterator>
|
||||
#include <functional>
|
||||
#include <algorithm>
|
||||
#include <vector>
|
||||
|
||||
template <size_t BucketSize,
|
||||
typename IterT,
|
||||
typename T = typename std::iterator_traits<IterT>::value_type,
|
||||
typename Compare = std::less<T>>
|
||||
void bucket_sort(IterT first, IterT last, Compare comp = Compare()) {
|
||||
const T min = *std::min_element(first, last), max = *std::max_element(first, last);
|
||||
const T range = max + 1 - min;
|
||||
const size_t bucket_num = (range - 1) / BucketSize + 1;
|
||||
|
||||
std::vector<std::vector<T>> buckets(bucket_num);
|
||||
for (auto b : buckets) {
|
||||
b.reserve(2 * BucketSize);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for (IterT i = first; i != last; ++i) {
|
||||
size_t idx = (*i - min) / BucketSize;
|
||||
buckets[idx].emplace_back(*i);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
IterT dest = first;
|
||||
for (auto b : buckets) {
|
||||
std::sort(b.begin(), b.end(), comp);
|
||||
std::copy(b.begin(), b.end(), dest);
|
||||
dest += b.size();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#endif // SORTS_BUCKET_SORT_HPP_
|
||||
|
||||
33
c-cpp/13_sorts/bucket_sort_test.cc
Normal file
33
c-cpp/13_sorts/bucket_sort_test.cc
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Created by Liam Huang (Liam0205) on 2018/10/26.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#include <iostream>
|
||||
#include <vector>
|
||||
#include <functional>
|
||||
|
||||
#include "bucket_sort.hpp"
|
||||
|
||||
template <size_t BucketSize,
|
||||
typename Container,
|
||||
typename T = typename Container::value_type,
|
||||
typename Compare = std::less<T>>
|
||||
void test_bucket_sort(Container cont, Compare comp = Compare()) {
|
||||
bucket_sort<BucketSize>(cont.begin(), cont.end(), comp);
|
||||
std::transform(cont.begin(), cont.end(), std::ostream_iterator<T>(std::cout, " "),
|
||||
[](T i){ return i; });
|
||||
std::cout << std::endl;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int main() {
|
||||
std::vector<int> test{3, 1, 4, 1, 5, 9, 2, 6, 5, 3, 5, 8, 9, 7, 9};
|
||||
|
||||
test_bucket_sort<2>(test); // 1 1 2 3 3 4 5 5 5 6 7 8 9 9 9
|
||||
test_bucket_sort<3>(test); // 1 1 2 3 3 4 5 5 5 6 7 8 9 9 9
|
||||
test_bucket_sort<4>(test); // 1 1 2 3 3 4 5 5 5 6 7 8 9 9 9
|
||||
test_bucket_sort<5>(test); // 1 1 2 3 3 4 5 5 5 6 7 8 9 9 9
|
||||
test_bucket_sort<6>(test); // 1 1 2 3 3 4 5 5 5 6 7 8 9 9 9
|
||||
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
40
c-cpp/13_sorts/counting_sort.hpp
Normal file
40
c-cpp/13_sorts/counting_sort.hpp
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Created by Liam Huang (Liam0205) on 2018/10/26.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef SORTS_COUNTING_SORT_HPP_
|
||||
#define SORTS_COUNTING_SORT_HPP_
|
||||
|
||||
#include <iterator>
|
||||
#include <functional>
|
||||
#include <algorithm>
|
||||
#include <vector>
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename IterT,
|
||||
typename T = typename std::iterator_traits<IterT>::value_type>
|
||||
void counting_sort(IterT first, IterT last) {
|
||||
const auto len = std::distance(first, last);
|
||||
if (len < 2) { return; }
|
||||
|
||||
const T max = *std::max_element(first, last);
|
||||
if (max == 0) { return; }
|
||||
|
||||
std::vector<size_t> counter(max + 1);
|
||||
for (IterT i = first; i != last; ++i) {
|
||||
++counter[*i];
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (size_t i = 1; i != max + 1; ++i) {
|
||||
const size_t j = max - i;
|
||||
counter[j] += counter[j + 1]; // Liam Huang: count of numbers that is not less than j.
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
std::vector<T> temp(len);
|
||||
for (IterT i = first; i != last; ++i) {
|
||||
temp[len - counter[*i]] = *i;
|
||||
--counter[*i]; // Liam Huang: stable for relative position.
|
||||
}
|
||||
std::copy(temp.begin(), temp.end(), first);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#endif // SORTS_COUNTING_SORT_HPP_
|
||||
|
||||
36
c-cpp/13_sorts/counting_sort_test.cc
Normal file
36
c-cpp/13_sorts/counting_sort_test.cc
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Created by Liam Huang (Liam0205) on 2018/10/26.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#include <iostream>
|
||||
#include <vector>
|
||||
#include <functional>
|
||||
|
||||
#include "counting_sort.hpp"
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Container,
|
||||
typename T = typename Container::value_type>
|
||||
void test_counting_sort(Container cont) {
|
||||
counting_sort(cont.begin(), cont.end());
|
||||
std::transform(cont.begin(), cont.end(), std::ostream_iterator<T>(std::cout, " "),
|
||||
[](T i){ return i; });
|
||||
std::cout << std::endl;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int main() {
|
||||
// Liam Huang: pi for test
|
||||
const std::vector<int> test1{3, 1, 4, 1, 5, 9, 2, 6, 5, 3, 5, 8, 9, 7, 9, 3};
|
||||
const std::vector<int> test2{2, 3, 8, 4, 6, 2, 6, 4, 3, 3, 8, 3, 2, 7, 9};
|
||||
const std::vector<int> test3{5, 0, 2, 8, 8, 4, 1, 9, 7, 1, 6, 9, 3, 9, 9};
|
||||
const std::vector<int> test4{3, 7, 5, 1, 0, 5, 8, 2, 0, 9, 7, 4, 9, 4, 4};
|
||||
const std::vector<int> test5{5, 9, 2, 3, 0, 7, 8, 1, 6, 4, 0, 6, 2, 8, 6};
|
||||
|
||||
test_counting_sort(test1); // 1 1 2 3 3 3 4 5 5 5 6 7 8 9 9 9
|
||||
test_counting_sort(test2); // 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 4 4 6 6 7 8 8 9
|
||||
test_counting_sort(test3); // 0 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 8 9 9 9 9
|
||||
test_counting_sort(test4); // 0 0 1 2 3 4 4 4 5 5 7 7 8 9 9
|
||||
test_counting_sort(test5); // 0 0 1 2 2 3 4 5 6 6 6 7 8 8 9
|
||||
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
96
c-cpp/15_bsearch/binary_search.c
Normal file
96
c-cpp/15_bsearch/binary_search.c
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,96 @@
|
||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||||
#include <stdlib.h>
|
||||
#include <stdbool.h>
|
||||
#include <string.h>
|
||||
|
||||
typedef int(*bs)(int *arr, int size, int val);
|
||||
|
||||
int binary_search_r(int *arr, int size, int val)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int mid = size / 2;
|
||||
int idx;
|
||||
|
||||
if (arr[mid] == val)
|
||||
return mid;
|
||||
|
||||
// mid == 0 means size == 1
|
||||
// so the only element in array doesn't equal to val
|
||||
if (!mid)
|
||||
return -1;
|
||||
|
||||
if (arr[mid] < val) {
|
||||
idx = binary_search_r(arr + mid + 1, size - mid - 1, val);
|
||||
if (idx != -1)
|
||||
idx += mid + 1;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
idx = binary_search_r(arr, mid, val);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return idx;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int binary_search_i(int *arr, int size, int val)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int low = 0, high = size - 1, mid;
|
||||
|
||||
while (low <= high) {
|
||||
mid = (low + high) / 2;
|
||||
if (arr[mid] == val)
|
||||
return mid;
|
||||
|
||||
if (arr[mid] < val)
|
||||
low = mid + 1;
|
||||
else
|
||||
high = mid - 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return -1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void iteratioin_test(bs binary_search)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int arr[10] = {1, 4, 5, 9, 12, 19, 21, 28, 31, 36};
|
||||
int idx;
|
||||
|
||||
idx = binary_search(arr, 10, 12);
|
||||
if (idx != -1)
|
||||
printf("find 12 at %d\n", idx);
|
||||
else
|
||||
printf("12 not in arr \n");
|
||||
|
||||
idx = binary_search(arr, 10, 13);
|
||||
if (idx != -1)
|
||||
printf("find 13 at %d\n", idx);
|
||||
else
|
||||
printf("13 not in arr \n");
|
||||
|
||||
idx = binary_search(arr, 10, 1);
|
||||
if (idx != -1)
|
||||
printf("find 1 at %d\n", idx);
|
||||
else
|
||||
printf("1 not in arr \n");
|
||||
|
||||
idx = binary_search(arr, 10, 36);
|
||||
if (idx != -1)
|
||||
printf("find 36 at %d\n", idx);
|
||||
else
|
||||
printf("36 not in arr \n");
|
||||
|
||||
idx = binary_search(arr, 10, 31);
|
||||
if (idx != -1)
|
||||
printf("find 31 at %d\n", idx);
|
||||
else
|
||||
printf("31 not in arr \n");
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
printf("=== Test iteration version:\n");
|
||||
iteratioin_test(binary_search_i);
|
||||
|
||||
printf("=== Test recursive version:\n");
|
||||
iteratioin_test(binary_search_r);
|
||||
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -8,19 +8,16 @@
|
||||
#include <iterator>
|
||||
#include <functional>
|
||||
|
||||
enum class BsearchPolicy { FIRST, LAST, UNSPECIFIED };
|
||||
|
||||
// Liam Huang: The algorithm works right with iterators that meet the ForwardIterator requirement,
|
||||
// but with a bad time complexity. For better performance, iterators should meet
|
||||
// the RandomAccessIterator requirement.
|
||||
template <typename IterT,
|
||||
typename ValueT = typename std::iterator_traits<IterT>::value_type,
|
||||
typename Compare>
|
||||
typename Compare = std::less<ValueT>>
|
||||
IterT bsearch(IterT first,
|
||||
IterT last,
|
||||
ValueT target,
|
||||
Compare comp,
|
||||
BsearchPolicy policy = BsearchPolicy::UNSPECIFIED) {
|
||||
Compare comp = Compare()) {
|
||||
IterT result = last;
|
||||
while (std::distance(first, last) > 0) {
|
||||
IterT mid = first + std::distance(first, last) / 2;
|
||||
@ -29,38 +26,12 @@ IterT bsearch(IterT first,
|
||||
} else if (comp(target, *mid)) {
|
||||
last = mid;
|
||||
} else { // equal
|
||||
if (policy == BsearchPolicy::FIRST) {
|
||||
if (mid == first or comp(*(mid - 1), *mid)) {
|
||||
result = mid;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
last = mid;
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if (policy == BsearchPolicy::LAST) {
|
||||
if (std::distance(mid, last) == 1 or comp(*mid, *(mid + 1))) {
|
||||
result = mid;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
first = mid + 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
result = mid;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
result = mid;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return result;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename IterT,
|
||||
typename ValueT = typename std::iterator_traits<IterT>::value_type,
|
||||
typename Compare = std::less<ValueT>>
|
||||
IterT bsearch(IterT first,
|
||||
IterT last,
|
||||
ValueT target,
|
||||
BsearchPolicy policy = BsearchPolicy::UNSPECIFIED) {
|
||||
return bsearch(first, last, target, Compare(), policy);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#endif // BSEARCH_BSEARCH_HPP_
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -8,10 +8,8 @@
|
||||
#include "bsearch.hpp"
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename VecT, typename T = typename VecT::value_type>
|
||||
void test_bsearch(const VecT& test,
|
||||
T target,
|
||||
BsearchPolicy policy = BsearchPolicy::UNSPECIFIED) {
|
||||
auto it = bsearch(test.begin(), test.end(), target, policy);
|
||||
void test_bsearch(const VecT& test, T target) {
|
||||
auto it = bsearch(test.begin(), test.end(), target);
|
||||
std::cout << std::distance(test.begin(), it) << std::endl;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -21,17 +19,9 @@ int main() {
|
||||
test_bsearch(test, 8); // 14
|
||||
test_bsearch(test, -1); // 14
|
||||
test_bsearch(test, 0); // 0, 1
|
||||
test_bsearch(test, 0, BsearchPolicy::FIRST); // 0
|
||||
test_bsearch(test, 0, BsearchPolicy::LAST); // 1
|
||||
test_bsearch(test, 4); // 5, 6
|
||||
test_bsearch(test, 4, BsearchPolicy::FIRST); // 5
|
||||
test_bsearch(test, 4, BsearchPolicy::LAST); // 6
|
||||
test_bsearch(test, 5); // 7, 8, 9, 10, 11
|
||||
test_bsearch(test, 5, BsearchPolicy::FIRST); // 7
|
||||
test_bsearch(test, 5, BsearchPolicy::LAST); // 11
|
||||
test_bsearch(test, 7); // 13
|
||||
test_bsearch(test, 7, BsearchPolicy::FIRST); // 13
|
||||
test_bsearch(test, 7, BsearchPolicy::LAST); // 13
|
||||
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
0
c-cpp/16_bsearch/.gitkeep
Normal file
0
c-cpp/16_bsearch/.gitkeep
Normal file
283
c-cpp/16_bsearch/bsearch_variant.c
Normal file
283
c-cpp/16_bsearch/bsearch_variant.c
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,283 @@
|
||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||||
#include <stdlib.h>
|
||||
#include <stdbool.h>
|
||||
#include <string.h>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
int binary_search(int *arr, int size, int val)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int low = 0, high = size - 1, mid;
|
||||
|
||||
while (low <= high) {
|
||||
mid = (low + high) / 2;
|
||||
if (arr[mid] == val)
|
||||
return mid;
|
||||
|
||||
if (arr[mid] < val)
|
||||
low = mid + 1;
|
||||
else
|
||||
high = mid - 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return -1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* find the first index with *val*
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This is a little tricky because the calculation of mid is integer based, it
|
||||
* will be cast to the lower bound of an integer.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* In case the [low, high] range is of size 1 or 2 and arr[mid] >= val, we will
|
||||
* have:
|
||||
*
|
||||
* mid = (low + high) / 2 = low
|
||||
* high = mid - 1 = low - 1 < low, which break the loop
|
||||
*
|
||||
*/
|
||||
int binary_search_first(int *arr, int size, int val)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int low = 0, high = size - 1, mid;
|
||||
|
||||
while (low <= high) {
|
||||
mid = (low + high) / 2;
|
||||
//printf("[%d-%d] %d\n", low, high, mid);
|
||||
|
||||
if (arr[mid] >= val)
|
||||
high = mid - 1;
|
||||
else
|
||||
low = mid + 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//printf("[%d-%d] %d\n", low, high, mid);
|
||||
if (arr[low] == val)
|
||||
return low;
|
||||
else
|
||||
return -1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int binary_search_last(int *arr, int size, int val)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int low = 0, high = size - 1, mid;
|
||||
|
||||
while (low <= high) {
|
||||
mid = (low + high) / 2;
|
||||
|
||||
if (arr[mid] <= val)
|
||||
low = mid + 1;
|
||||
else
|
||||
high = mid - 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (arr[high] == val)
|
||||
return high;
|
||||
else
|
||||
return -1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int binary_search_first_r(int *arr, int size, int val)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int mid = size / 2;
|
||||
int idx;
|
||||
|
||||
if (size <= 0)
|
||||
return -1;
|
||||
|
||||
// we find *val* at mid, try first half
|
||||
if (arr[mid] == val) {
|
||||
idx = binary_search_first_r(arr, mid, val);
|
||||
return idx != -1 ? idx : mid;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// mid == 0 means size == 1
|
||||
// so the only element in array doesn't equal to val
|
||||
if (!mid)
|
||||
return -1;
|
||||
|
||||
if (arr[mid] < val) {
|
||||
idx = binary_search_first_r(arr + mid + 1, size - mid - 1, val);
|
||||
if (idx != -1)
|
||||
idx += mid + 1;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
idx = binary_search_first_r(arr, mid, val);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return idx;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int binary_search_last_r(int *arr, int size, int val)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int mid = size / 2;
|
||||
int idx;
|
||||
|
||||
if (size <= 0)
|
||||
return -1;
|
||||
|
||||
// we find *val* at mid, try last half
|
||||
if (arr[mid] == val) {
|
||||
idx = binary_search_last_r(arr+mid+1, size-mid-1, val);
|
||||
if (idx != -1)
|
||||
mid += idx + 1;
|
||||
return mid;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// mid == 0 means size == 1
|
||||
// so the only element in array doesn't equal to val
|
||||
if (!mid)
|
||||
return -1;
|
||||
|
||||
if (arr[mid] < val) {
|
||||
idx = binary_search_last_r(arr + mid + 1, size - mid - 1, val);
|
||||
if (idx != -1)
|
||||
idx += mid + 1;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
idx = binary_search_last_r(arr, mid, val);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return idx;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int binary_search_first_bigger(int *arr, int size, int val)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int low = 0, high = size - 1, mid;
|
||||
|
||||
while (low <= high) {
|
||||
mid = (low + high) / 2;
|
||||
|
||||
if (arr[mid] >= val) {
|
||||
if (mid == 0 || arr[mid-1] < val)
|
||||
return mid;
|
||||
high = mid - 1;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
low = mid + 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return -1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int binary_search_first_bigger_r(int *arr, int size, int val)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int mid = size / 2;
|
||||
int idx;
|
||||
|
||||
if (size <= 0)
|
||||
return -1;
|
||||
|
||||
if (arr[mid] >= val) {
|
||||
// find one bigger than val, try first half
|
||||
idx = binary_search_first_bigger_r(arr, mid, val);
|
||||
if (idx == -1)
|
||||
idx = mid;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// the bigger one may sit in second half
|
||||
idx = binary_search_first_bigger_r(arr + mid + 1, size - mid - 1, val);
|
||||
if (idx != -1)
|
||||
idx += mid + 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return idx;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int binary_search_last_smaller(int *arr, int size, int val)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int low = 0, high = size - 1, mid;
|
||||
|
||||
while (low <= high) {
|
||||
mid = (low + high) / 2;
|
||||
|
||||
if (arr[mid] <= val) {
|
||||
if (mid == 0 || arr[mid+1] > val)
|
||||
return mid;
|
||||
low = mid + 1;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
high = mid - 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return -1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int binary_search_last_smaller_r(int *arr, int size, int val)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int mid = size / 2;
|
||||
int idx;
|
||||
|
||||
if (size <= 0)
|
||||
return -1;
|
||||
|
||||
if (arr[mid] <= val) {
|
||||
// find one smaller than val, try second half
|
||||
idx = binary_search_last_smaller_r(arr + mid + 1, size - mid - 1, val);
|
||||
if (idx != -1)
|
||||
idx += mid + 1;
|
||||
else
|
||||
idx = mid;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// the smaller one may sit in first half
|
||||
idx = binary_search_last_smaller_r(arr, mid, val);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return idx;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
int arr[10] = {1, 4, 5, 9, 12, 14, 19, 19, 31, 36};
|
||||
int idx;
|
||||
|
||||
printf("Test Array:\n");
|
||||
for (idx = 0; idx < 10; idx++)
|
||||
printf("%8d", arr[idx]);
|
||||
printf("\n");
|
||||
|
||||
idx = binary_search_first(arr, 10, 19);
|
||||
if (idx != -1)
|
||||
printf("first 19 at %d\n", idx);
|
||||
else
|
||||
printf("19 not in arr \n");
|
||||
|
||||
idx = binary_search_first_r(arr, 10, 19);
|
||||
if (idx != -1)
|
||||
printf("first 19 at %d\n", idx);
|
||||
else
|
||||
printf("19 not in arr \n");
|
||||
|
||||
idx = binary_search_last(arr, 10, 19);
|
||||
if (idx != -1)
|
||||
printf("last 19 at %d\n", idx);
|
||||
else
|
||||
printf("19 not in arr \n");
|
||||
|
||||
idx = binary_search_last_r(arr, 10, 19);
|
||||
if (idx != -1)
|
||||
printf("last 19 at %d\n", idx);
|
||||
else
|
||||
printf("19 not in arr \n");
|
||||
|
||||
idx = binary_search_first_bigger(arr, 10, 12);
|
||||
if (idx != -1)
|
||||
printf("first bigger 12 at %d\n", idx);
|
||||
else
|
||||
printf("12 not in arr \n");
|
||||
|
||||
idx = binary_search_first_bigger_r(arr, 10, 12);
|
||||
if (idx != -1)
|
||||
printf("first bigger 12 at %d\n", idx);
|
||||
else
|
||||
printf("12 not in arr \n");
|
||||
|
||||
idx = binary_search_last_smaller(arr, 10, 12);
|
||||
if (idx != -1)
|
||||
printf("last smaller 12 at %d\n", idx);
|
||||
else
|
||||
printf("12 not in arr \n");
|
||||
|
||||
idx = binary_search_last_smaller_r(arr, 10, 12);
|
||||
if (idx != -1)
|
||||
printf("last smaller 12 at %d\n", idx);
|
||||
else
|
||||
printf("12 not in arr \n");
|
||||
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
90
c-cpp/16_bsearch/bsearch_varients.hpp
Normal file
90
c-cpp/16_bsearch/bsearch_varients.hpp
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,90 @@
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Created by Liam Huang (Liam0205) on 2018/10/26.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef BSEARCH_BSEARCH_VARIENTS_HPP_
|
||||
#define BSEARCH_BSEARCH_VARIENTS_HPP_
|
||||
|
||||
#include <iterator>
|
||||
#include <functional>
|
||||
|
||||
enum class BsearchPolicy { UNSPECIFIED, FIRST, LAST, FIRST_NOT_LESS, LAST_NOT_GREATER };
|
||||
|
||||
// Liam Huang: The algorithm works right with iterators that meet the ForwardIterator requirement,
|
||||
// but with a bad time complexity. For better performance, iterators should meet
|
||||
// the RandomAccessIterator requirement.
|
||||
template <typename IterT,
|
||||
typename ValueT = typename std::iterator_traits<IterT>::value_type,
|
||||
typename Compare>
|
||||
IterT bsearch(IterT first,
|
||||
IterT last,
|
||||
ValueT target,
|
||||
Compare comp,
|
||||
BsearchPolicy policy = BsearchPolicy::UNSPECIFIED) {
|
||||
IterT result = last;
|
||||
while (std::distance(first, last) > 0) {
|
||||
IterT mid = first + std::distance(first, last) / 2;
|
||||
if (policy == BsearchPolicy::FIRST_NOT_LESS) {
|
||||
if (!comp(*mid, target)) {
|
||||
if (mid == first or comp(*(mid - 1), target)) {
|
||||
result = mid;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
last = mid;
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
first = mid + 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if (policy == BsearchPolicy::LAST_NOT_GREATER) {
|
||||
if (comp(target, *mid)) {
|
||||
last = mid;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if (std::distance(mid, last) == 1 or comp(target, *(mid + 1))) {
|
||||
result = mid;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
first = mid + 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else { // policy == UNSPECIFIED or FIRST or LAST
|
||||
if (comp(*mid, target)) {
|
||||
first = mid + 1;
|
||||
} else if (comp(target, *mid)) {
|
||||
last = mid;
|
||||
} else { // equal
|
||||
if (policy == BsearchPolicy::FIRST) {
|
||||
if (mid == first or comp(*(mid - 1), *mid)) {
|
||||
result = mid;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
last = mid;
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if (policy == BsearchPolicy::LAST) {
|
||||
if (std::distance(mid, last) == 1 or comp(*mid, *(mid + 1))) {
|
||||
result = mid;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
first = mid + 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
result = mid;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return result;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename IterT,
|
||||
typename ValueT = typename std::iterator_traits<IterT>::value_type,
|
||||
typename Compare = std::less<ValueT>>
|
||||
IterT bsearch(IterT first,
|
||||
IterT last,
|
||||
ValueT target,
|
||||
BsearchPolicy policy = BsearchPolicy::UNSPECIFIED) {
|
||||
return bsearch(first, last, target, Compare(), policy);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#endif // BSEARCH_BSEARCH_VARIENTS_HPP_
|
||||
|
||||
41
c-cpp/16_bsearch/bsearch_varients_test.cc
Normal file
41
c-cpp/16_bsearch/bsearch_varients_test.cc
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Created by Liam Huang (Liam0205) on 2018/10/26.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#include <iostream>
|
||||
#include <vector>
|
||||
|
||||
#include "bsearch_varients.hpp"
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename VecT, typename T = typename VecT::value_type>
|
||||
void test_bsearch(const VecT& test,
|
||||
T target,
|
||||
BsearchPolicy policy = BsearchPolicy::UNSPECIFIED) {
|
||||
auto it = bsearch(test.begin(), test.end(), target, policy);
|
||||
std::cout << std::distance(test.begin(), it) << std::endl;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int main() {
|
||||
std::vector<int> test{0, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 6, 8}; // std::less<int>()
|
||||
|
||||
test_bsearch(test, 8); // 14
|
||||
test_bsearch(test, -1); // 14
|
||||
test_bsearch(test, 0); // 0, 1
|
||||
test_bsearch(test, 0, BsearchPolicy::FIRST); // 0
|
||||
test_bsearch(test, 0, BsearchPolicy::LAST); // 1
|
||||
test_bsearch(test, 4); // 5, 6
|
||||
test_bsearch(test, 4, BsearchPolicy::FIRST); // 5
|
||||
test_bsearch(test, 4, BsearchPolicy::LAST); // 6
|
||||
test_bsearch(test, 5); // 7, 8, 9, 10, 11
|
||||
test_bsearch(test, 5, BsearchPolicy::FIRST); // 7
|
||||
test_bsearch(test, 5, BsearchPolicy::LAST); // 11
|
||||
test_bsearch(test, 7, BsearchPolicy::FIRST_NOT_LESS); // 13
|
||||
test_bsearch(test, 7, BsearchPolicy::LAST_NOT_GREATER); // 12
|
||||
test_bsearch(test, 7, BsearchPolicy::FIRST); // 14
|
||||
test_bsearch(test, 8); // 13
|
||||
test_bsearch(test, 8, BsearchPolicy::FIRST); // 13
|
||||
test_bsearch(test, 8, BsearchPolicy::LAST); // 13
|
||||
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
0
c-cpp/17_skiplist/.gitkeep
Normal file
0
c-cpp/17_skiplist/.gitkeep
Normal file
186
c-cpp/17_skiplist/skiplist.hpp
Normal file
186
c-cpp/17_skiplist/skiplist.hpp
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,186 @@
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Created by Liam Huang (Liam0205) on 2018/10/29.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef SKIPLIST_SKIPLIST_HPP_
|
||||
#define SKIPLIST_SKIPLIST_HPP_
|
||||
|
||||
#include <functional>
|
||||
#include <type_traits>
|
||||
#include <vector>
|
||||
#include <chrono>
|
||||
#include <random>
|
||||
#include <initializer_list>
|
||||
#include <limits>
|
||||
#include <iostream>
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Value>
|
||||
class skiplist {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
using value_type = Value;
|
||||
using hash_type = std::hash<value_type>;
|
||||
using key_type = typename hash_type::result_type;
|
||||
using size_type = size_t;
|
||||
|
||||
private:
|
||||
struct InternalNode {
|
||||
value_type value;
|
||||
const key_type key;
|
||||
std::vector<InternalNode*> forwards; // pointers to successor nodes
|
||||
|
||||
InternalNode(const key_type& k, const size_type lv)
|
||||
: value(), key(k), forwards(lv, nullptr) {}
|
||||
InternalNode(const value_type& v, const size_type lv)
|
||||
: value(v), key(hash_type()(value)), forwards(lv, nullptr) {}
|
||||
};
|
||||
using node_type = InternalNode;
|
||||
|
||||
private:
|
||||
const size_type MAX_LEVEL = 16;
|
||||
const double PROBABILITY = 0.5;
|
||||
const unsigned int seed =
|
||||
std::chrono::system_clock::now().time_since_epoch().count();
|
||||
mutable
|
||||
std::default_random_engine generator = std::default_random_engine(seed);
|
||||
mutable
|
||||
std::binomial_distribution<size_type> distribution =
|
||||
std::binomial_distribution<size_type>(MAX_LEVEL - 1, PROBABILITY);
|
||||
node_type* head = nullptr;
|
||||
node_type* nil = nullptr;
|
||||
static const value_type default_value;
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
skiplist() {
|
||||
key_type head_key = std::numeric_limits<key_type>::min();
|
||||
key_type nil_key = std::numeric_limits<key_type>::max();
|
||||
head = new node_type(head_key, MAX_LEVEL);
|
||||
nil = new node_type(nil_key, MAX_LEVEL);
|
||||
std::fill(head->forwards.begin(), head->forwards.end(), nil);
|
||||
}
|
||||
skiplist(std::initializer_list<value_type> init) : skiplist() {
|
||||
for (const value_type& v : init) {
|
||||
insert(v);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
skiplist(const skiplist& other) = delete;
|
||||
skiplist(skiplist&& other) :
|
||||
MAX_LEVEL(std::move(other.MAX_LEVEL)),
|
||||
PROBABILITY(std::move(other.PROBABILITY)),
|
||||
seed(std::move(other.seed)),
|
||||
generator(std::move(other.generator)),
|
||||
distribution(std::move(other.distribution)),
|
||||
head(other.head),
|
||||
nil(other.nil) {
|
||||
other.head = nullptr;
|
||||
other.nil = nullptr;
|
||||
}
|
||||
~skiplist() {
|
||||
node_type* node = head;
|
||||
while (nullptr != node and nullptr != node->forwards[0]) {
|
||||
node_type* tmp = node;
|
||||
node = node->forwards[0];
|
||||
delete tmp;
|
||||
}
|
||||
delete node;
|
||||
}
|
||||
skiplist& operator=(const skiplist& other) = delete;
|
||||
skiplist& operator=(skiplist&& other) = delete;
|
||||
|
||||
private:
|
||||
inline size_type get_random_level() const {
|
||||
return distribution(generator);
|
||||
}
|
||||
static size_type get_node_level(const node_type* node) {
|
||||
return node->forwards.size();
|
||||
}
|
||||
static node_type* make_node(const value_type& v, const size_type lv) {
|
||||
return new node_type(v, lv);
|
||||
}
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief returns a pointer to the first node such that
|
||||
* node->key == hash_type()(v) and node->value == v.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
node_type* get_first_equal(const value_type& v) const {
|
||||
const key_type target = hash_type()(v);
|
||||
node_type* x = head;
|
||||
for (size_type i = get_node_level(head); i > 0; --i) {
|
||||
while (x->forwards[i - 1]->key < target or
|
||||
x->forwards[i - 1]->key == target and x->forwards[i - 1]->value != v) {
|
||||
x = x->forwards[i - 1];
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return x->forwards[0];
|
||||
}
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief returns a collection of nodes.
|
||||
* returns[i] is the pointer to the last node at level i + 1
|
||||
* such that returns[i]->key < hash_type()(v) or
|
||||
* returns[i]->key == hash_type()(v) but returns[i]->value != v.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
std::vector<node_type*> get_predecessors(const value_type& v) const {
|
||||
const key_type target = hash_type()(v);
|
||||
std::vector<node_type*> results(get_node_level(head), nullptr);
|
||||
node_type* x = head;
|
||||
for (size_type i = get_node_level(head); i > 0; --i) {
|
||||
while (x->forwards[i - 1]->key < target or
|
||||
x->forwards[i - 1]->key == target and x->forwards[i - 1]->value != v) {
|
||||
x = x->forwards[i - 1];
|
||||
}
|
||||
results[i - 1] = x;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return results;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
const value_type& find(const value_type& target) {
|
||||
node_type* x = get_first_equal(target);
|
||||
if (nullptr != x and nil != x and x->value == target) {
|
||||
return x->value;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
return default_value;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
void insert(const value_type& value) {
|
||||
std::vector<node_type*> preds = get_predecessors(value);
|
||||
const size_type new_node_lv = get_random_level();
|
||||
node_type* new_node = make_node(value, new_node_lv);
|
||||
for (size_type i = 0; i != new_node_lv; ++i) {
|
||||
new_node->forwards[i] = preds[i]->forwards[i];
|
||||
preds[i]->forwards[i] = new_node;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
void erase(const value_type& value) {
|
||||
std::vector<node_type*> preds = get_predecessors(value);
|
||||
|
||||
node_type* node = preds[0]->forwards[0];
|
||||
if (node == nil or node->value != value) { return; }
|
||||
|
||||
for (size_type i = 0; i != get_node_level(node); ++i) {
|
||||
preds[i]->forwards[i] = node->forwards[i];
|
||||
}
|
||||
delete node;
|
||||
}
|
||||
void print(std::ostream& os) const {
|
||||
node_type* list = head->forwards[0];
|
||||
os << "{";
|
||||
|
||||
while (list != nil) {
|
||||
os << "key: " << list->key << " value: " << list->value
|
||||
<< " level: " << get_node_level(list);
|
||||
|
||||
list = list->forwards[0];
|
||||
|
||||
if (list != nil) os << " : ";
|
||||
|
||||
os << "\n";
|
||||
}
|
||||
os << "}\n";
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Value>
|
||||
const typename skiplist<Value>::value_type skiplist<Value>::default_value =
|
||||
typename skiplist<Value>::value_type();
|
||||
|
||||
#endif // SKIPLIST_SKIPLIST_HPP_
|
||||
|
||||
67
c-cpp/17_skiplist/skiplist_test.cc
Normal file
67
c-cpp/17_skiplist/skiplist_test.cc
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,67 @@
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Created by Liam Huang (Liam0205) on 2018/10/30.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#include <iostream>
|
||||
#include <string>
|
||||
|
||||
#include "skiplist.hpp"
|
||||
|
||||
int main() {
|
||||
// 1. Initialize a skip list for test
|
||||
// * default constructor
|
||||
// * constructor with initializer list
|
||||
// * insert
|
||||
skiplist<std::string> ss{"1", "2", "3", "4", "5"};
|
||||
|
||||
// 1a. show
|
||||
// * print
|
||||
ss.print(std::cout);
|
||||
std::cout << std::endl;
|
||||
|
||||
// 2. move construction
|
||||
// * move constructor
|
||||
skiplist<std::string> s(std::move(ss));
|
||||
|
||||
// 2a. show
|
||||
// * print
|
||||
s.print(std::cout);
|
||||
std::cout << std::endl;
|
||||
|
||||
// 3.a find something doesn't exist.
|
||||
// * find
|
||||
auto f = s.find("0");
|
||||
if (!f.empty()) {
|
||||
std::cout << "Node found!\nvalue: " << f << '\n';
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
std::cout << "Node NOT found!\n";
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 3.b find something does exist.
|
||||
// * find
|
||||
auto ff = s.find("1");
|
||||
if (!ff.empty()) {
|
||||
std::cout << "Node found!\tvalue: " << ff << '\n';
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
std::cout << "Node NOT found!\n";
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 4. insert() - reassign
|
||||
s.insert("TEST");
|
||||
|
||||
// 4a. print()
|
||||
s.print(std::cout);
|
||||
std::cout << std::endl;
|
||||
|
||||
// 5. erase()
|
||||
s.erase("TEST");
|
||||
|
||||
// 5a. print();
|
||||
s.print(std::cout);
|
||||
std::cout << std::endl;
|
||||
|
||||
std::cout << "\nDone!\n";
|
||||
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
// 6. destructor
|
||||
}
|
||||
366
c-cpp/17_skiplist/skiplist_tr.hpp
Normal file
366
c-cpp/17_skiplist/skiplist_tr.hpp
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,366 @@
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Created by Liam Huang (Liam0205) on 2018/10/30.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef SKIPLIST_SKIPLIST_TR_HPP_
|
||||
#define SKIPLIST_SKIPLIST_TR_HPP_
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef LIAM_UT_DEBUG_
|
||||
#include <assert.h>
|
||||
#include <iostream>
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#include <set>
|
||||
#include <vector>
|
||||
#include <list>
|
||||
#include <functional>
|
||||
#include <type_traits>
|
||||
#include <random>
|
||||
#include <limits>
|
||||
#include <algorithm>
|
||||
#include <initializer_list>
|
||||
#include <iterator>
|
||||
|
||||
namespace skiplist_detail {
|
||||
template <typename Key, typename Value>
|
||||
struct InternalNode {
|
||||
using iterator = typename std::list<InternalNode>::iterator;
|
||||
const Key key;
|
||||
std::multiset<Value> values;
|
||||
std::vector<iterator> forwards;
|
||||
|
||||
InternalNode() = delete;
|
||||
explicit InternalNode(const Key& k) : key(k) {}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename IntType>
|
||||
class random_level {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
mutable std::random_device rd;
|
||||
mutable std::mt19937 gen = std::mt19937(rd());
|
||||
mutable std::binomial_distribution<IntType> dist;
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
random_level(IntType max_level, double prob) : dist(max_level - 1, prob) {}
|
||||
inline IntType operator()() const { return dist(gen); }
|
||||
};
|
||||
} // namespace skiplist_detail
|
||||
|
||||
enum class erase_policy { ALL, SINGLE };
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Value,
|
||||
typename Hash = std::hash<Value>,
|
||||
size_t Factor = 2>
|
||||
class skiplist {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
using value_type = Value;
|
||||
using size_type = size_t;
|
||||
using hasher = Hash;
|
||||
using hash_type = typename Hash::result_type;
|
||||
using compare = std::less<hash_type>;
|
||||
using node_type = skiplist_detail::InternalNode<hash_type, value_type>;
|
||||
using container = std::list<node_type>;
|
||||
using iterator = typename container::iterator;
|
||||
using const_iterator = typename container::const_iterator;
|
||||
static_assert(std::is_same<iterator, typename node_type::iterator>::value,
|
||||
"STATIC ASSERT FAILED! iterator type differs.");
|
||||
|
||||
private:
|
||||
size_type max_lv_ = 2;
|
||||
double prob_ = 0.5;
|
||||
mutable skiplist_detail::random_level<size_type> rl_;
|
||||
container cont_;
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
skiplist() : rl_(max_lv_, prob_) {
|
||||
init_internally();
|
||||
}
|
||||
explicit skiplist(const size_type max_lv, const double prob = 0.5)
|
||||
: max_lv_(max_lv), prob_(prob), rl_(max_lv_, prob_) {
|
||||
init_internally();
|
||||
}
|
||||
skiplist(skiplist&& other) = default;
|
||||
skiplist& operator=(skiplist&& other) = default;
|
||||
~skiplist() = default;
|
||||
template <typename InputIt>
|
||||
skiplist(InputIt first, InputIt last) : skiplist() {
|
||||
using value_type_in_iter = typename std::iterator_traits<InputIt>::value_type;
|
||||
static_assert(std::is_same<value_type, value_type_in_iter>::value,
|
||||
"STATIC ASSERT FAILED! Value in InputIt should be the same to value_type.");
|
||||
for (InputIt i = first; i != last; ++i) {
|
||||
insert(*i);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
skiplist(std::initializer_list<value_type> init) : skiplist(init.begin(), init.end()) {}
|
||||
|
||||
private: // noncopyable
|
||||
skiplist(const skiplist&) = delete;
|
||||
skiplist& operator=(const skiplist&) = delete;
|
||||
|
||||
private:
|
||||
void init_internally() {
|
||||
const hash_type tail_key = std::numeric_limits<hash_type>::max();
|
||||
node_type tail(tail_key);
|
||||
tail.forwards.resize(max_lv_);
|
||||
std::fill(tail.forwards.begin(), tail.forwards.end(), cont_.end());
|
||||
cont_.insert(cont_.begin(), std::move(tail));
|
||||
|
||||
const hash_type head_key = std::numeric_limits<hash_type>::min();
|
||||
node_type head(head_key);
|
||||
head.forwards.resize(max_lv_);
|
||||
cont_.insert(cont_.begin(), std::move(head));
|
||||
std::fill(cont_.begin()->forwards.begin(), cont_.begin()->forwards.end(),
|
||||
std::next(cont_.begin()));
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef LIAM_UT_DEBUG_
|
||||
assert(cont_.begin()->key == head_key);
|
||||
for (auto it : cont_.begin()->forwards) {
|
||||
assert(it->key == tail_key);
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (auto it : std::next(cont_.begin())->forwards) {
|
||||
assert(it == cont_.end());
|
||||
}
|
||||
std::cerr << "UT_DEBUG: all assert in init_internally() success!\n";
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief return a const_iterator points to the last element
|
||||
* such that its hash_key <= target_hash_key
|
||||
*/
|
||||
const_iterator find_helper(const hash_type& key) const {
|
||||
#ifdef LIAM_UT_DEBUG_
|
||||
std::cerr << "Keys contained in the list: ";
|
||||
for (auto node : cont_) {
|
||||
std::cerr << node.key << ' ';
|
||||
}
|
||||
std::cerr << '\n';
|
||||
std::cerr << "Target key: " << key << '\n';
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
const_iterator iter = begin();
|
||||
for (size_type i = 0; i != max_lv_; ++i) {
|
||||
size_type focus = max_lv_ - 1 - i;
|
||||
// invariant: iter->key <= key
|
||||
while (not compare()(key, iter->forwards[focus]->key)) {
|
||||
#ifdef LIAM_UT_DEBUG_
|
||||
std::cerr << "i: " << i << " focus: " << focus << ". "
|
||||
<< "since iter->forwards[focus]->key[" << iter->forwards[focus]->key
|
||||
<< "] <= key[" << key << "], ";
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
iter = iter->forwards[focus];
|
||||
#ifdef LIAM_UT_DEBUG_
|
||||
std::cerr << "step forward iter to [" << iter->key << "]\n";
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
}
|
||||
// result: iter->key <= key < iter->forwards[focus]->key
|
||||
#ifdef LIAM_UT_DEBUG_
|
||||
std::cerr << "The following fact holds at level " << focus
|
||||
<< ": iter->key[" << iter->key << "] <= key["
|
||||
<< key << "] < iter->forwards[focus]->key[" << iter->forwards[focus]->key
|
||||
<<"].\n";
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
}
|
||||
return iter;
|
||||
}
|
||||
std::vector<iterator> find_predecessors(const hash_type& key, const size_type& lv) {
|
||||
#ifdef LIAM_UT_DEBUG_
|
||||
std::cerr << "Keys contained in the list: ";
|
||||
for (auto node : cont_) {
|
||||
std::cerr << node.key << ' ';
|
||||
}
|
||||
std::cerr << '\n';
|
||||
std::cerr << "Target key: " << key << '\n';
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
std::vector<iterator> res;
|
||||
res.resize(lv + 1);
|
||||
iterator iter = begin();
|
||||
for (size_type i = 0; i != max_lv_; ++i) {
|
||||
size_type focus = max_lv_ - 1 - i;
|
||||
#ifdef LIAM_UT_DEBUG_
|
||||
std::cerr << "i: " << i << " focus: " << focus << ".\n";
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
// invariant: iter->key < key
|
||||
while (compare()(iter->forwards[focus]->key, key)) {
|
||||
#ifdef LIAM_UT_DEBUG_
|
||||
std::cerr << "since iter->forwards[focus]->key[" << iter->forwards[focus]->key
|
||||
<< "] < key[" << key << "], ";
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
iter = iter->forwards[focus];
|
||||
#ifdef LIAM_UT_DEBUG_
|
||||
std::cerr << "step forward iter to [" << iter->key << "]\n";
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
}
|
||||
// result: iter->key < key <= iter->forwards[focus]->key
|
||||
#ifdef LIAM_UT_DEBUG_
|
||||
std::cerr << "The following fact holds at level " << focus
|
||||
<< ": iter->key[" << iter->key << "] < key[" << key
|
||||
<< "] <= iter->forwards[focus]->key[" << iter->forwards[focus]->key
|
||||
<<"].\n";
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
if (focus < lv + 1) {
|
||||
res[focus] = iter;
|
||||
#ifdef LIAM_UT_DEBUG_
|
||||
std::cerr << "predecessor at level [" << focus
|
||||
<< "] has been recorded, while level upper limit is " << lv <<".\n";
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return res;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
size_type size() const {
|
||||
return cont_.size() - 2;
|
||||
}
|
||||
bool empty() const {
|
||||
return size() == 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
iterator begin() {
|
||||
return cont_.begin();
|
||||
}
|
||||
const_iterator begin() const {
|
||||
return cont_.cbegin();
|
||||
}
|
||||
const_iterator cbegin() const {
|
||||
return cont_.cbegin();
|
||||
}
|
||||
iterator end() {
|
||||
return cont_.end();
|
||||
}
|
||||
const_iterator end() const {
|
||||
return cont_.cend();
|
||||
}
|
||||
const_iterator cend() const {
|
||||
return cont_.cend();
|
||||
}
|
||||
void grow(const size_type new_max_lv) {
|
||||
if (max_lv_ < new_max_lv) {
|
||||
#ifdef LIAM_UT_DEBUG_
|
||||
std::cerr << "grow from [" << max_lv_ << "] to ["
|
||||
<< new_max_lv << "]!\n";
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
max_lv_ = new_max_lv;
|
||||
|
||||
iterator tail = std::prev(cont_.end());
|
||||
auto beg_tail = tail->forwards.end();
|
||||
tail->forwards.resize(max_lv_, cont_.end());
|
||||
|
||||
iterator head = cont_.begin();
|
||||
auto beg_head = head->forwards.end();
|
||||
head->forwards.resize(max_lv_, tail);
|
||||
|
||||
return;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
#ifdef LIAM_UT_DEBUG_
|
||||
std::cerr << "abandon growing!\n";
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
void grow() {
|
||||
grow(Factor * max_lv_);
|
||||
}
|
||||
size_type capability() const {
|
||||
return std::pow(Factor, max_lv_);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
const_iterator find(const value_type& target) const {
|
||||
#ifdef LIAM_UT_DEBUG_
|
||||
std::cerr << "finding [" << target << "]!\n";
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
const hash_type key = hasher()(target);
|
||||
const_iterator iter = find_helper(key);
|
||||
return (iter->key == key) ? iter : cont_.end();
|
||||
}
|
||||
void insert(const value_type& target) {
|
||||
#ifdef LIAM_UT_DEBUG_
|
||||
std::cerr << "inserting [" << target << "]!\n";
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
if (size() > static_cast<double>(Factor - 1) / Factor * capability()) {
|
||||
#ifdef LIAM_UT_DEBUG_
|
||||
std::cerr << "size[" << size() << "], Factor[" << Factor << "], capability[" << capability() << "]!\n";
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
grow();
|
||||
}
|
||||
const hash_type key = hasher()(target);
|
||||
const size_type lv = rl_();
|
||||
std::vector<iterator> predecessors = find_predecessors(key, lv);
|
||||
if (predecessors[0]->forwards[0]->key == key) { // key already in skiplist
|
||||
#ifdef LIAM_UT_DEBUG_
|
||||
std::cerr << "key [" << key << "] already in the skiplist, insert directly!\n";
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
predecessors[0]->forwards[0]->values.insert(target);
|
||||
return;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
#ifdef LIAM_UT_DEBUG_
|
||||
std::cerr << "key [" << key << "] not in the skiplist, insert a new node!\n";
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
node_type node(key);
|
||||
node.forwards.resize(lv + 1);
|
||||
node.values.insert(target);
|
||||
iterator inserted = cont_.insert(predecessors[0]->forwards[0], std::move(node));
|
||||
for (size_type i = 0; i != lv + 1; ++i) {
|
||||
inserted->forwards[i] = predecessors[i]->forwards[i];
|
||||
predecessors[i]->forwards[i] = inserted;
|
||||
}
|
||||
#ifdef LIAM_UT_DEBUG_
|
||||
assert(inserted->forwards[0] == std::next(inserted));
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
void erase(const value_type& target,
|
||||
const erase_policy policy = erase_policy::ALL) {
|
||||
#ifdef LIAM_UT_DEBUG_
|
||||
std::cerr << "erasing [" << target << "]!\n";
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
const hash_type key = hasher()(target);
|
||||
std::vector<iterator> predecessors = find_predecessors(key, max_lv_);
|
||||
if (predecessors[0]->forwards[0]->key == key) { // hit
|
||||
#ifdef LIAM_UT_DEBUG_
|
||||
std::cerr << "key [" << key << "] is in the skiplist!\n";
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
iterator found = predecessors[0]->forwards[0];
|
||||
for (auto iter = found->values.begin(); iter != found->values.end(); ) {
|
||||
if (policy == erase_policy::ALL) {
|
||||
if (*iter == target) {
|
||||
iter = found->values.erase(iter);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
++iter;
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if (policy == erase_policy::SINGLE) {
|
||||
if (*iter == target) {
|
||||
found->values.erase(iter);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
#ifdef LIAM_UT_DEBUG_
|
||||
std::cerr << "target(s) removed!\n";
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
if (found->values.empty()) {
|
||||
const size_type lvp1 = found->forwards.size(); // lv plus 1
|
||||
for (size_type i = 0; i != lvp1; ++i) {
|
||||
predecessors[i]->forwards[i] = found->forwards[i];
|
||||
}
|
||||
cont_.erase(found);
|
||||
#ifdef LIAM_UT_DEBUG_
|
||||
std::cerr << "empty node removed!\n";
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
return;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
#ifdef LIAM_UT_DEBUG_
|
||||
std::cerr << "key [" << key << "] is not in the skiplist, do nothing!\n";
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
#endif // SKIPLIST_SKIPLIST_TR_HPP_
|
||||
|
||||
107
c-cpp/17_skiplist/skiplist_tr_test.cc
Normal file
107
c-cpp/17_skiplist/skiplist_tr_test.cc
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,107 @@
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Created by Liam Huang (Liam0205) on 2018/10/30.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#include <assert.h>
|
||||
|
||||
#include <iostream>
|
||||
#include <map>
|
||||
#include <string>
|
||||
|
||||
#include "skiplist_tr.hpp"
|
||||
|
||||
int main() {
|
||||
// 1. UT for skiplist_detail::random_level
|
||||
skiplist_detail::random_level<size_t> rl(5, 0.5);
|
||||
std::map<size_t, size_t> hist;
|
||||
for (size_t i = 0; i != 10000; ++i) {
|
||||
++hist[rl()];
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (auto p : hist) {
|
||||
std::cout << p.first << ' ' << std::string(p.second / 100, '*') << '\n';
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 2. UT for skiplist(), init_internally(), size(), empty()
|
||||
skiplist<std::string> sl_default;
|
||||
assert(sl_default.empty());
|
||||
// 2.1. UT for grow with abandon
|
||||
sl_default.grow(1);
|
||||
assert(sl_default.capability() == 4);
|
||||
// 2.2. UT for grow
|
||||
sl_default.grow(10);
|
||||
assert(sl_default.capability() == 1024);
|
||||
|
||||
// 3. UT for constructor of initializer_list and InputIt, init_internally(), insert(),
|
||||
// find_predecessors()
|
||||
skiplist<std::string> sl{"hello", "world", "!"};
|
||||
assert(not sl.empty());
|
||||
assert(3 == sl.size());
|
||||
|
||||
// 4. UT for find() find_helper()
|
||||
auto search = sl_default.find("nonexist");
|
||||
assert(search == sl_default.cend());
|
||||
assert(search == sl_default.end());
|
||||
search = sl.find("hello");
|
||||
assert(search != sl.cend());
|
||||
assert(search != sl.end());
|
||||
search = sl.find("nonexist");
|
||||
assert(search == sl.cend());
|
||||
assert(search == sl.end());
|
||||
|
||||
// 5. UT for insert(), find_predecessors()
|
||||
// 5.1. UT for insert a already-exist item
|
||||
sl.insert("hello");
|
||||
search = sl.find("hello");
|
||||
assert(search != sl.cend());
|
||||
assert(search != sl.end());
|
||||
// 5.2. UT for insert a new incoming item
|
||||
search = sl.find("now exist");
|
||||
assert(search == sl.cend());
|
||||
assert(search == sl.end());
|
||||
sl.insert("now exist");
|
||||
search = sl.find("now exist");
|
||||
assert(search != sl.cend());
|
||||
assert(search != sl.end());
|
||||
|
||||
// 6. UT for erase(), find_predecessors()
|
||||
sl.insert("hello");
|
||||
sl.insert("hello");
|
||||
sl.insert("hello");
|
||||
sl.insert("hello");
|
||||
// 6.1. UT for erase single item
|
||||
sl.erase("hello", erase_policy::SINGLE);
|
||||
search = sl.find("hello");
|
||||
assert(search != sl.cend());
|
||||
assert(search != sl.end());
|
||||
// 6.2. UT for erase all items
|
||||
sl.erase("hello", erase_policy::ALL);
|
||||
search = sl.find("hello");
|
||||
assert(search == sl.cend());
|
||||
assert(search == sl.end());
|
||||
// 6.3 UT for erase non-exist item
|
||||
sl.erase("nonexist");
|
||||
|
||||
// 7. UT for insert() behind erase()
|
||||
// 7.1. different word
|
||||
sl.insert("world");
|
||||
search = sl.find("world");
|
||||
assert(search != sl.cend());
|
||||
assert(search != sl.end());
|
||||
assert(search->values.count("world") == 2);
|
||||
// 7.1. same word, also UT for grow()
|
||||
search = sl.find("hello");
|
||||
assert(search == sl.cend());
|
||||
assert(search == sl.end());
|
||||
sl.insert("hello");
|
||||
sl.insert("hello");
|
||||
sl.insert("hello");
|
||||
sl.insert("hello");
|
||||
sl.insert("hello");
|
||||
search = sl.find("hello");
|
||||
assert(search != sl.cend());
|
||||
assert(search != sl.end());
|
||||
assert(search->values.count("hello") == 5);
|
||||
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
// 8. UT for ~skiplist()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
63
f21
Normal file
63
f21
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
|
||||
// A Stack based C++ program to find next
|
||||
// greater element for all array elements
|
||||
// in same order as input.
|
||||
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
|
||||
|
||||
using namespace std;
|
||||
|
||||
/* prints element and NGE pair for all
|
||||
elements of arr[] of size n */
|
||||
void printNGE(int arr[], int n)
|
||||
{
|
||||
stack<int> s;
|
||||
unordered_map<int, int> mp;
|
||||
|
||||
/* push the first element to stack */
|
||||
s.push(arr[0]);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// iterate for rest of the elements
|
||||
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (s.empty()) {
|
||||
s.push(arr[i]);
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* if stack is not empty, then
|
||||
pop an element from stack.
|
||||
If the popped element is smaller
|
||||
than next, then
|
||||
a) print the pair
|
||||
b) keep popping while elements are
|
||||
smaller and stack is not empty */
|
||||
while (s.empty() == false && s.top() < arr[i]) {
|
||||
mp[s.top()] = arr[i];
|
||||
s.pop();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* push next to stack so that we can find
|
||||
next smaller for it */
|
||||
s.push(arr[i]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* After iterating over the loop, the remaining
|
||||
elements in stack do not have the next smaller
|
||||
element, so print -1 for them */
|
||||
while (s.empty() == false) {
|
||||
mp[s.top()] = -1;
|
||||
s.pop();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i=0; i<n; i++)
|
||||
cout << arr[i] << " ---> " << mp[arr[i]] << endl;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Driver program to test above functions */
|
||||
int main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
int arr[] = { 11, 13, 21, 3 };
|
||||
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
|
||||
printNGE(arr, n);
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -45,3 +45,111 @@ func bs(a []int, v int, low, high int) int {
|
||||
return bs(a, v, mid+1, high)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//查找第一个等于给定值的元素
|
||||
func BinarySearchFirst(a []int, v int) int {
|
||||
n := len(a)
|
||||
if n == 0 {
|
||||
return -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
low := 0
|
||||
high := n - 1
|
||||
for low <= high {
|
||||
mid := (low + high) >> 1
|
||||
if a[mid] > v {
|
||||
high = mid - 1
|
||||
} else if a[mid] < v {
|
||||
low = mid + 1
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if mid == 0 || a[mid-1] != v {
|
||||
return mid
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
high = mid - 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//查找最后一个值等于给定值的元素
|
||||
func BinarySearchLast(a []int, v int) int {
|
||||
n := len(a)
|
||||
if n == 0 {
|
||||
return -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
low := 0
|
||||
high := n - 1
|
||||
for low <= high {
|
||||
mid := (low + high) >> 1
|
||||
if a[mid] > v {
|
||||
high = mid - 1
|
||||
} else if a[mid] < v {
|
||||
low = mid + 1
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if mid == n-1 || a[mid+1] != v {
|
||||
return mid
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
low = mid + 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//查找第一个大于等于给定值的元素
|
||||
func BinarySearchFirstGT(a []int, v int) int {
|
||||
n := len(a)
|
||||
if n == 0 {
|
||||
return -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
low := 0
|
||||
high := n - 1
|
||||
for low <= high {
|
||||
mid := (high + low) >> 1
|
||||
if a[mid] > v {
|
||||
high = mid - 1
|
||||
} else if a[mid] < v {
|
||||
low = mid + 1
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if mid != n-1 && a[mid+1] > v {
|
||||
return mid + 1
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
low = mid + 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//查找最后一个小于等于给定值的元素
|
||||
func BinarySearchLastLT(a []int, v int) int {
|
||||
n := len(a)
|
||||
if n == 0 {
|
||||
return -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
low := 0
|
||||
high := n - 1
|
||||
for low <= high {
|
||||
mid := (low + high) >> 1
|
||||
if a[mid] > v {
|
||||
high = mid - 1
|
||||
} else if a[mid] < v {
|
||||
low = mid + 1
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if mid == 0 || a[mid-1] < v {
|
||||
return mid - 1
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
high = mid - 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -25,3 +25,79 @@ func TestBinarySearchRecursive(t *testing.T) {
|
||||
t.Fatal(BinarySearch(a, 4))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func TestBinarySearchFirst(t *testing.T) {
|
||||
var a []int
|
||||
|
||||
a = []int{1, 2, 2, 2, 3, 4}
|
||||
if BinarySearchFirst(a, 2) != 1 {
|
||||
t.Fatal(BinarySearchFirst(a, 2))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
a = []int{1, 2, 2, 2, 3, 4}
|
||||
if BinarySearchFirst(a, 3) != 4 {
|
||||
t.Fatal(BinarySearchFirst(a, 3))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func TestBinarySearchLast(t *testing.T) {
|
||||
var a []int
|
||||
|
||||
a = []int{1, 2, 2, 2, 3, 4}
|
||||
if BinarySearchLast(a, 2) != 3 {
|
||||
t.Fatal(BinarySearchLast(a, 2))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
a = []int{1, 2, 2, 2, 3, 4}
|
||||
if BinarySearchLast(a, 3) != 4 {
|
||||
t.Fatal(BinarySearchLast(a, 3))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func TestBinarySearchFirstGT(t *testing.T) {
|
||||
var a []int
|
||||
|
||||
a = []int{1, 2, 2, 2, 3, 4}
|
||||
if BinarySearchFirstGT(a, 2) != 4 {
|
||||
t.Fatal(BinarySearchFirstGT(a, 2))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
a = []int{1, 2, 2, 2, 3, 4}
|
||||
if BinarySearchFirstGT(a, 1) != 1 {
|
||||
t.Fatal(BinarySearchFirstGT(a, 1))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
a = []int{1, 2, 2, 2, 3, 4}
|
||||
if BinarySearchFirstGT(a, 3) != 5 {
|
||||
t.Fatal(BinarySearchFirstGT(a, 3))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
a = []int{1, 2, 2, 2, 3, 4}
|
||||
if BinarySearchFirstGT(a, 4) != -1 {
|
||||
t.Fatal(BinarySearchFirstGT(a, 4))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func TestBinarySearchLastLT(t *testing.T) {
|
||||
var a []int
|
||||
|
||||
a = []int{1, 2, 2, 2, 3, 4}
|
||||
if BinarySearchLastLT(a, 2) != 0 {
|
||||
t.Fatal(BinarySearchLastLT(a, 2))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
a = []int{1, 2, 2, 2, 3, 4}
|
||||
if BinarySearchLastLT(a, 1) != -1 {
|
||||
t.Fatal(BinarySearchLastLT(a, 1))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
a = []int{1, 2, 2, 2, 3, 4}
|
||||
if BinarySearchLastLT(a, 3) != 3 {
|
||||
t.Fatal(BinarySearchLastLT(a, 3))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
a = []int{1, 2, 2, 2, 3, 4}
|
||||
if BinarySearchLastLT(a, 4) != 4 {
|
||||
t.Fatal(BinarySearchLastLT(a, 4))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
177
go/17_skiplist/skiplist.go
Normal file
177
go/17_skiplist/skiplist.go
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,177 @@
|
||||
package _7_skiplist
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"math"
|
||||
"math/rand"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
//最高层数
|
||||
MAX_LEVEL = 16
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
//跳表节点结构体
|
||||
type skipListNode struct {
|
||||
//跳表保存的值
|
||||
v interface{}
|
||||
//用于排序的分值
|
||||
score int
|
||||
//层高
|
||||
level int
|
||||
//每层前进指针
|
||||
forwards []*skipListNode
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//新建跳表节点
|
||||
func newSkipListNode(v interface{}, score, level int) *skipListNode {
|
||||
return &skipListNode{v: v, score: score, forwards: make([]*skipListNode, level, level), level: level}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//跳表结构体
|
||||
type SkipList struct {
|
||||
//跳表头结点
|
||||
head *skipListNode
|
||||
//跳表当前层数
|
||||
level int
|
||||
//跳表长度
|
||||
length int
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//实例化跳表对象
|
||||
func NewSkipList() *SkipList {
|
||||
//头结点,便于操作
|
||||
head := newSkipListNode(0, math.MinInt32, MAX_LEVEL)
|
||||
return &SkipList{head, 1, 0}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//获取跳表长度
|
||||
func (sl *SkipList) Length() int {
|
||||
return sl.length
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//获取跳表层级
|
||||
func (sl *SkipList) Level() int {
|
||||
return sl.level
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//插入节点到跳表中
|
||||
func (sl *SkipList) Insert(v interface{}, score int) int {
|
||||
if nil == v {
|
||||
return 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//查找插入位置
|
||||
cur := sl.head
|
||||
//记录每层的路径
|
||||
update := [MAX_LEVEL]*skipListNode{}
|
||||
i := MAX_LEVEL - 1
|
||||
for ; i >= 0; i-- {
|
||||
for nil != cur.forwards[i] {
|
||||
if cur.forwards[i].v == v {
|
||||
return 2
|
||||
}
|
||||
if cur.forwards[i].score > score {
|
||||
update[i] = cur
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
cur = cur.forwards[i]
|
||||
}
|
||||
if nil == cur.forwards[i] {
|
||||
update[i] = cur
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//通过随机算法获取该节点层数
|
||||
level := 1
|
||||
for i := 1; i < MAX_LEVEL; i++ {
|
||||
if rand.Int31()%7 == 1 {
|
||||
level++
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//创建一个新的跳表节点
|
||||
newNode := newSkipListNode(v, score, level)
|
||||
|
||||
//原有节点连接
|
||||
for i := 0; i <= level-1; i++ {
|
||||
next := update[i].forwards[i]
|
||||
update[i].forwards[i] = newNode
|
||||
newNode.forwards[i] = next
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//如果当前节点的层数大于之前跳表的层数
|
||||
//更新当前跳表层数
|
||||
if level > sl.level {
|
||||
sl.level = level
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//更新跳表长度
|
||||
sl.length++
|
||||
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//查找
|
||||
func (sl *SkipList) Find(v interface{}, score int) *skipListNode {
|
||||
if nil == v || sl.length == 0 {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
cur := sl.head
|
||||
for i := sl.level - 1; i >= 0; i-- {
|
||||
for nil != cur.forwards[i] {
|
||||
if cur.forwards[i].score == score && cur.forwards[i].v == v {
|
||||
return cur.forwards[i]
|
||||
} else if cur.forwards[i].score > score {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
cur = cur.forwards[i]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//删除节点
|
||||
func (sl *SkipList) Delete(v interface{}, score int) int {
|
||||
if nil == v {
|
||||
return 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//查找前驱节点
|
||||
cur := sl.head
|
||||
//记录前驱路径
|
||||
update := [MAX_LEVEL]*skipListNode{}
|
||||
for i := sl.level - 1; i >= 0; i-- {
|
||||
update[i] = sl.head
|
||||
for nil != cur.forwards[i] {
|
||||
if cur.forwards[i].score == score && cur.forwards[i].v == v {
|
||||
update[i] = cur
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
cur = cur.forwards[i]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
cur = update[0].forwards[0]
|
||||
for i := cur.level - 1; i >= 0; i-- {
|
||||
if update[i] == sl.head && cur.forwards[i] == nil {
|
||||
sl.level = i
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if nil == update[i].forwards[i] {
|
||||
update[i].forwards[i] = nil
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
update[i].forwards[i] = update[i].forwards[i].forwards[i]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
sl.length--
|
||||
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (sl *SkipList) String() string {
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf("level:%+v, length:%+v", sl.level, sl.length)
|
||||
}
|
||||
38
go/17_skiplist/skiplist_test.go
Normal file
38
go/17_skiplist/skiplist_test.go
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
|
||||
package _7_skiplist
|
||||
|
||||
import "testing"
|
||||
|
||||
func TestSkipList(t *testing.T) {
|
||||
sl := NewSkipList()
|
||||
|
||||
sl.Insert("leo", 95)
|
||||
t.Log(sl.head.forwards[0])
|
||||
t.Log(sl.head.forwards[0].forwards[0])
|
||||
t.Log(sl)
|
||||
t.Log("-----------------------------")
|
||||
|
||||
sl.Insert("jack", 88)
|
||||
t.Log(sl.head.forwards[0])
|
||||
t.Log(sl.head.forwards[0].forwards[0])
|
||||
t.Log(sl.head.forwards[0].forwards[0].forwards[0])
|
||||
t.Log(sl)
|
||||
t.Log("-----------------------------")
|
||||
|
||||
sl.Insert("lily", 100)
|
||||
t.Log(sl.head.forwards[0])
|
||||
t.Log(sl.head.forwards[0].forwards[0])
|
||||
t.Log(sl.head.forwards[0].forwards[0].forwards[0])
|
||||
t.Log(sl.head.forwards[0].forwards[0].forwards[0].forwards[0])
|
||||
t.Log(sl)
|
||||
t.Log("-----------------------------")
|
||||
|
||||
t.Log(sl.Find("jack", 88))
|
||||
t.Log("-----------------------------")
|
||||
|
||||
sl.Delete("leo", 95)
|
||||
t.Log(sl.head.forwards[0])
|
||||
t.Log(sl.head.forwards[0].forwards[0])
|
||||
t.Log(sl.head.forwards[0].forwards[0].forwards[0])
|
||||
t.Log(sl)
|
||||
t.Log("-----------------------------")
|
||||
}
|
||||
90
go/binarysearch2.go
Normal file
90
go/binarysearch2.go
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,90 @@
|
||||
package binarySearch
|
||||
|
||||
//查找第一个值等于给定值得元素
|
||||
func BinarySearch2(nums []int, value int) int {
|
||||
length := len(nums)
|
||||
start := 0
|
||||
end := length - 1
|
||||
for start <= end {
|
||||
mid := (start + end) / 2
|
||||
if nums[mid] > value {
|
||||
end = mid - 1
|
||||
} else if nums[mid] < value {
|
||||
start = mid + 1
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
for mid >= 0 {
|
||||
if nums[mid-1] == value {
|
||||
mid--
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
return mid
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 查找最后一个值等于给定值的元素
|
||||
func BinarySearch3(nums []int, value int) int {
|
||||
start := 0
|
||||
end := len(nums) - 1
|
||||
for start <= end {
|
||||
mid := (start + end) / 2
|
||||
if nums[mid] > value {
|
||||
end = mid - 1
|
||||
} else if nums[mid] < value {
|
||||
start = mid + 1
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
for mid < len(nums) {
|
||||
if nums[mid+1] == value {
|
||||
mid++
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
return mid
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 查找第一个大于等于给定值的元素
|
||||
func BinarySearch4(nums []int, value int) int {
|
||||
start := 0
|
||||
end := len(nums) - 1
|
||||
for start <= end {
|
||||
mid := (start + end) >> 1
|
||||
if nums[mid] < value {
|
||||
start = mid + 1
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
for mid >= 0 {
|
||||
if nums[mid-1] >= value {
|
||||
mid--
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
return mid
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 查找最后一个小于等于给定值的元素
|
||||
func BinarySearch5(nums []int, value int) int {
|
||||
start := 0
|
||||
end := len(nums) - 1
|
||||
for start <= end {
|
||||
mid := (start + end) >> 1
|
||||
if nums[mid] > value {
|
||||
end = mid - 1
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
for mid < len(nums) {
|
||||
if nums[mid+1] <= value {
|
||||
mid++
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
return mid
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
119
java/17_skiplist/SkipList.java
Normal file
119
java/17_skiplist/SkipList.java
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,119 @@
|
||||
package skiplist;
|
||||
|
||||
import java.util.Random;
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 跳表的一种实现方法。
|
||||
* 跳表中存储的是正整数,并且存储的是不重复的。
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Author:ZHENG
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public class SkipList {
|
||||
|
||||
private static final int MAX_LEVEL = 16;
|
||||
|
||||
private int levelCount = 1;
|
||||
|
||||
private Node head = new Node(); // 带头链表
|
||||
|
||||
private Random r = new Random();
|
||||
|
||||
public Node find(int value) {
|
||||
Node p = head;
|
||||
for (int i = levelCount - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
|
||||
while (p.forwards[i] != null && p.forwards[i].data < value) {
|
||||
p = p.forwards[i];
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (p.forwards[0] != null && p.forwards[0].data == value) {
|
||||
return p.forwards[0];
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
return null;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public void insert(int value) {
|
||||
int level = randomLevel();
|
||||
Node newNode = new Node();
|
||||
newNode.data = value;
|
||||
newNode.maxLevel = level;
|
||||
Node update[] = new Node[level];
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < level; ++i) {
|
||||
update[i] = head;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Node p = head;
|
||||
for (int i = level - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
|
||||
while (p.forwards[i] != null && p.forwards[i].data < value) {
|
||||
p = p.forwards[i];
|
||||
}
|
||||
update[i] = p;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < level; ++i) {
|
||||
newNode.forwards[i] = update[i].forwards[i];
|
||||
update[i].forwards[i] = newNode;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (levelCount < level) levelCount = level;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public void delete(int value) {
|
||||
Node[] update = new Node[levelCount];
|
||||
Node p = head;
|
||||
for (int i = levelCount - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
|
||||
while (p.forwards[i] != null && p.forwards[i].data < value) {
|
||||
p = p.forwards[i];
|
||||
}
|
||||
update[i] = p;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (p.forwards[0] != null && p.forwards[0].data == value) {
|
||||
for (int i = levelCount - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
|
||||
if (update[i].forwards[i] != null && update[i].forwards[i].data == value) {
|
||||
update[i].forwards[i] = update[i].forwards[i].forwards[i];
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
private int randomLevel() {
|
||||
int level = 1;
|
||||
for (int i = 1; i < MAX_LEVEL; ++i) {
|
||||
if (r.nextInt() % 2 == 1) {
|
||||
level++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return level;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public void printAll() {
|
||||
Node p = head;
|
||||
while (p.forwards[0] != null) {
|
||||
System.out.print(p.forwards[0] + " ");
|
||||
p = p.forwards[0];
|
||||
}
|
||||
System.out.println();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public class Node {
|
||||
private int data = -1;
|
||||
private Node forwards[] = new Node[MAX_LEVEL];
|
||||
private int maxLevel = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
@Override
|
||||
public String toString() {
|
||||
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
|
||||
builder.append("{ data: ");
|
||||
builder.append(data);
|
||||
builder.append("; levels: ");
|
||||
builder.append(maxLevel);
|
||||
builder.append(" }");
|
||||
|
||||
return builder.toString();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
27
javascript/15_binary/binaryFind.js
Normal file
27
javascript/15_binary/binaryFind.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 二分查找
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Author: nameczz
|
||||
*/
|
||||
// 数组必须有序 不存在重复
|
||||
const biaryFind = (sortedArr, target) => {
|
||||
if (sortedArr.length === 0) return -1
|
||||
let low = 0
|
||||
let high = sortedArr.length - 1
|
||||
while (low <= high) {
|
||||
const mid = Math.floor((low + high) / 2)
|
||||
if (target === sortedArr[mid]) {
|
||||
return mid
|
||||
} else if (target < sortedArr[mid]) {
|
||||
high = mid - 1
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
low = mid + 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
const arr = [1, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 10, 11, 23, 42, 44, 54, 56, 77, 102]
|
||||
console.log(biaryFind(arr, 44))
|
||||
console.log(biaryFind(arr, 1))
|
||||
console.log(biaryFind(arr, 102))
|
||||
console.log(biaryFind(arr, 1111))
|
||||
90
javascript/16_binary/binary-find.js
Normal file
90
javascript/16_binary/binary-find.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,90 @@
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 二分查找
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Author: nameczz
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// 查找第一个等于给定值
|
||||
const biaryFindFirst = (sortedArr, target) => {
|
||||
if (sortedArr.length === 0) return -1
|
||||
let low = 0
|
||||
let high = sortedArr.length - 1
|
||||
while (low <= high) {
|
||||
const mid = Math.floor((low + high) / 2)
|
||||
|
||||
if (target < sortedArr[mid]) {
|
||||
high = mid - 1
|
||||
} else if (target > sortedArr[mid]) {
|
||||
low = mid + 1
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if (mid === 0 || sortedArr[mid - 1] < target) return mid
|
||||
high = mid - 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 查找最后一个相等的数
|
||||
const biaryFindLast = (sortedArr, target) => {
|
||||
if (sortedArr.length === 0) return -1
|
||||
let low = 0
|
||||
let high = sortedArr.length - 1
|
||||
while (low <= high) {
|
||||
const mid = Math.floor((low + high) / 2)
|
||||
if (target < sortedArr[mid]) {
|
||||
high = mid - 1
|
||||
} else if (target > sortedArr[mid]) {
|
||||
low = mid + 1
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if (mid === sortedArr.length - 1 || sortedArr[mid + 1] > target) return mid
|
||||
low = mid + 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 查找第一个大于等于给定值的元素
|
||||
const biaryFindFistBig = (sortedArr, target) => {
|
||||
if (sortedArr.length === 0) return -1
|
||||
let low = 0
|
||||
let high = sortedArr.length - 1
|
||||
while (low <= high) {
|
||||
const mid = Math.floor((low + high) / 2)
|
||||
if (target <= sortedArr[mid]) {
|
||||
if (mid === 0 || sortedArr[mid - 1] < target) return mid
|
||||
high = mid - 1
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
low = mid + 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 查找最后一个小于等于给定值的元素
|
||||
const biaryFindLastSmall = (sortedArr, target) => {
|
||||
if (sortedArr.length === 0) return -1
|
||||
let low = 0
|
||||
let high = sortedArr.length - 1
|
||||
while (low <= high) {
|
||||
const mid = Math.floor((low + high) / 2)
|
||||
if (sortedArr[mid] > target) {
|
||||
high = mid - 1
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if (mid === sortedArr.length - 1 || sortedArr[mid + 1] > target) return mid
|
||||
low = mid + 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 6, 7, 8, 8, 9]
|
||||
const first = biaryFindFirst(arr, 4)
|
||||
console.log(`FindFirst: ${first}`)
|
||||
|
||||
const last = biaryFindLast(arr, 4)
|
||||
console.log(`FindLast: ${last}`)
|
||||
const FisrtBig = biaryFindFistBig(arr, 5)
|
||||
console.log(`FindFisrtBig: ${FisrtBig}`)
|
||||
const LastSmall = biaryFindLastSmall(arr, 4)
|
||||
console.log(`FindLastSmall: ${LastSmall}`)
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
||||
# 排序(上)
|
||||
# 排序(平方时间复杂度排序算法)
|
||||
|
||||
| 排序算法 | 时间复杂度 | 是否基于比较 |
|
||||
|---------|----|----|
|
||||
|
||||
0
notes/12_sorts/.gitkeep
Normal file
0
notes/12_sorts/.gitkeep
Normal file
176
notes/12_sorts/readme.md
Normal file
176
notes/12_sorts/readme.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,176 @@
|
||||
# 排序(线性对数时间复杂度排序算法)
|
||||
|
||||
开篇问题:如何在 $O(n)$ 时间复杂度内寻找一个无序数组中第 K 大的元素?
|
||||
|
||||
## 归并排序
|
||||
|
||||
* 归并排序使用了「分治」思想(Divide and Conquer)
|
||||
* 分:把数组分成前后两部分,分别排序
|
||||
* 合:将有序的两部分合并
|
||||
|
||||
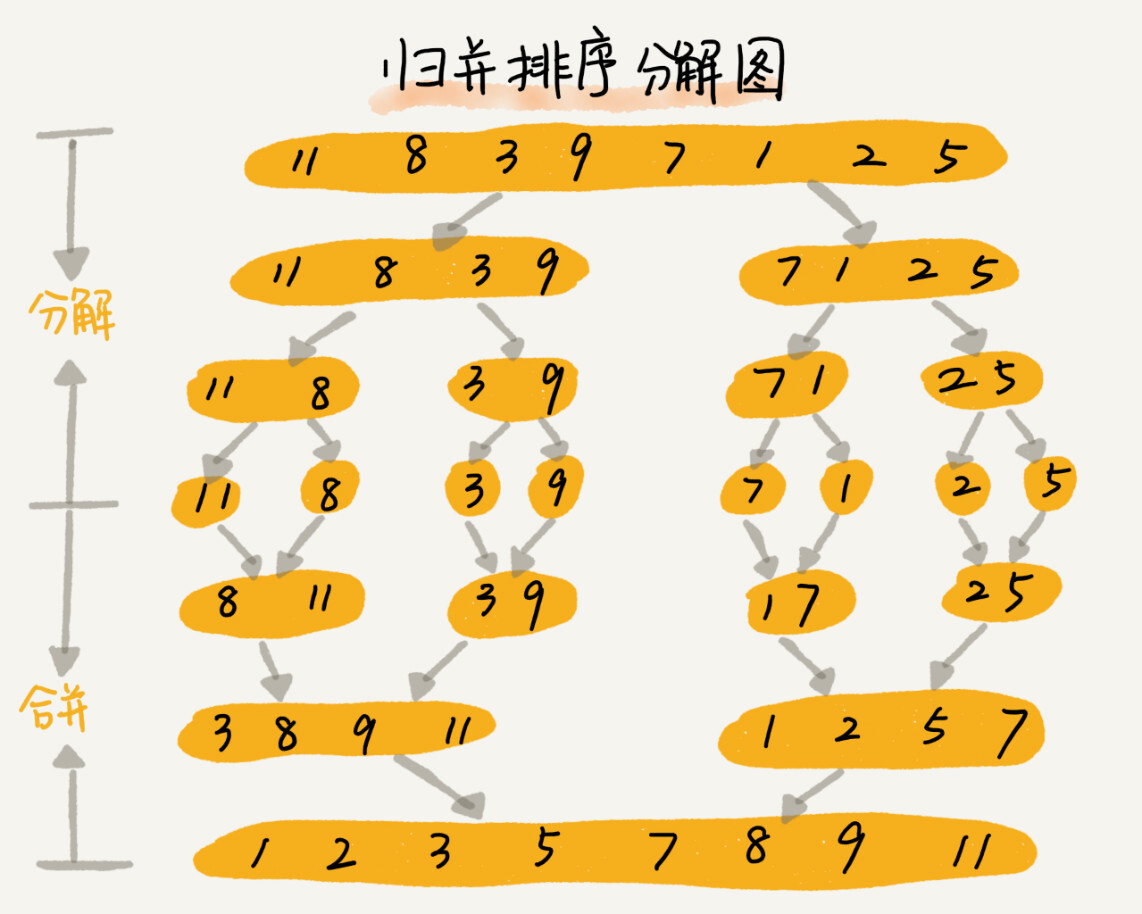
|
||||
|
||||
* 分治与递归
|
||||
* 分治:解决问题的处理办法
|
||||
* 递归:实现算法的手段
|
||||
* ——分治算法经常用递归来实现
|
||||
* 递归实现:
|
||||
* 终止条件:区间 `[first, last)` 内不足 2 个元素
|
||||
* 递归公式:`merge_sort(first, last) = merge(merge_sort(first, mid), merge_sort(mid, last))`,其中 `mid = first + (last - first) / 2`
|
||||
|
||||
C++ 实现:
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
template <typename FrwdIt,
|
||||
typename T = typename std::iterator_traits<FrwdIt>::value_type,
|
||||
typename BinaryPred = std::less<T>>
|
||||
void merge_sort(FrwdIt first, FrwdIt last, BinaryPred comp = BinaryPred()) {
|
||||
const auto len = std::distance(first, last);
|
||||
if (len <= 1) { return; }
|
||||
auto cut = first + len / 2;
|
||||
merge_sort(first, cut, comp);
|
||||
merge_sort(cut, last, comp);
|
||||
std::vector<T> tmp;
|
||||
tmp.reserve(len);
|
||||
detail::merge(first, cut, cut, last, std::back_inserter(tmp), comp);
|
||||
std::copy(tmp.begin(), tmp.end(), first);
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这里涉及到一个 `merge` 的过程,它的实现大致是:
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
namespace detail {
|
||||
template <typename InputIt1, typename InputIt2, typename OutputIt,
|
||||
typename BinaryPred = std::less<typename std::iterator_traits<InputIt1>::value_type>>
|
||||
OutputIt merge(InputIt1 first1, InputIt1 last1,
|
||||
InputIt2 first2, InputIt2 last2,
|
||||
OutputIt d_first,
|
||||
BinaryPred comp = BinaryPred()) {
|
||||
for (; first1 != last1; ++d_first) {
|
||||
if (first2 == last2) {
|
||||
return std::copy(first1, last1, d_first);
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (comp(*first2, *first1)) {
|
||||
*d_first = *first2;
|
||||
++first2;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
*d_first = *first1;
|
||||
++first1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return std::copy(first2, last2, d_first);
|
||||
}
|
||||
} // namespace detail
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
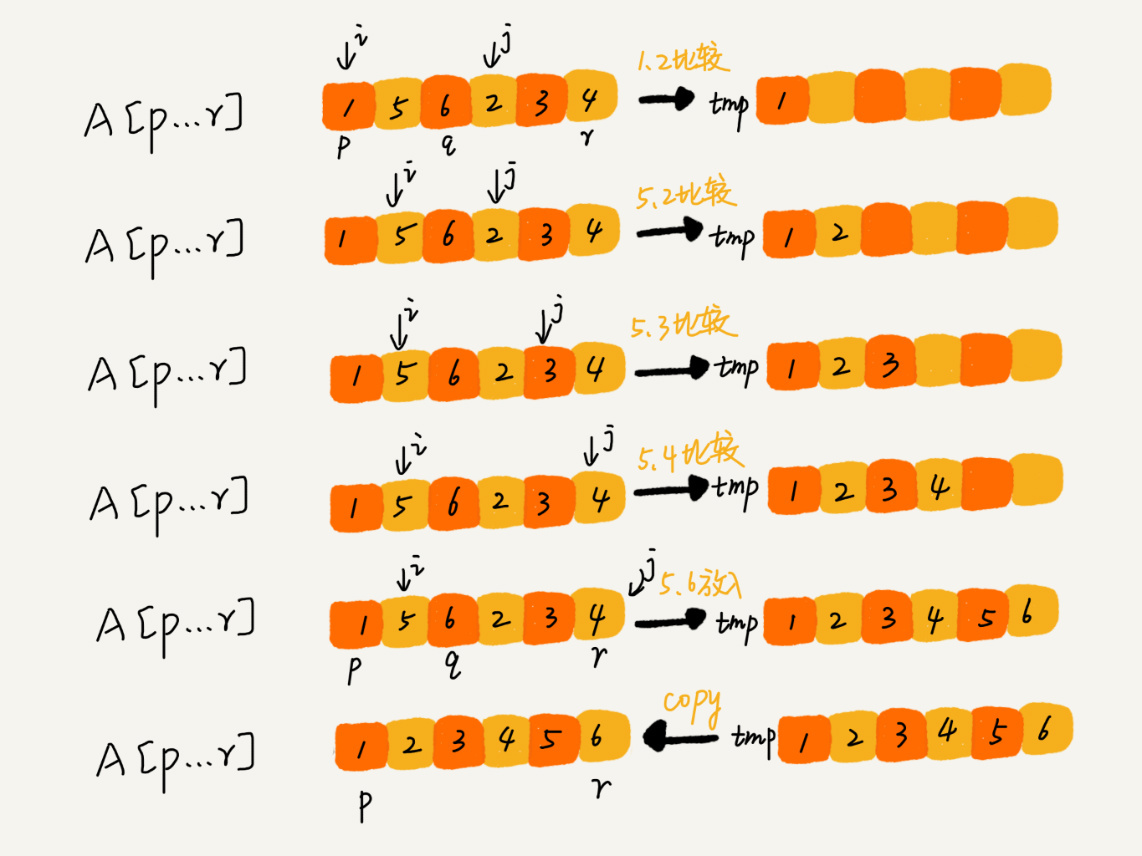
|
||||
|
||||
### 算法分析
|
||||
|
||||
* 稳定性
|
||||
* 由于 `comp` 是严格偏序,所以 `!comp(*first2, *first1)` 时,取用 `first1` 的元素放入 `d_first` 保证了算法稳定性
|
||||
* 时间复杂度
|
||||
* 定义 $T(n)$ 表示问题规模为 $n$ 时算法的耗时,
|
||||
* 有递推公式:$T(n) = 2T(n/2) + n$
|
||||
* 展开得 $T(n) = 2^{k}T(1) + k * n$
|
||||
* 考虑 $k$ 是递归深度,它的值是 $\log_2 n$,因此 $T(n) = n + n\log_2 n$
|
||||
* 因此,归并排序的时间复杂度为 $\Theta(n\log n)$
|
||||
* 空间复杂度
|
||||
* 一般来说,空间复杂度是 $\Theta(n)$
|
||||
|
||||
## 快速排序(quick sort,快排)
|
||||
|
||||
原理:
|
||||
|
||||
* 在待排序区间 `[first, last)` 中选取一个元素,称为主元(pivot,枢轴)
|
||||
* 对待排序区间进行划分,使得 `[first, cut)` 中的元素满足 `comp(element, pivot)` 而 `[cut, last)` 中的元素不满足 `comp(element, pivot)`
|
||||
* 对划分的两个区间,继续划分,直到区间 `[first, last)` 内不足 2 个元素
|
||||
|
||||
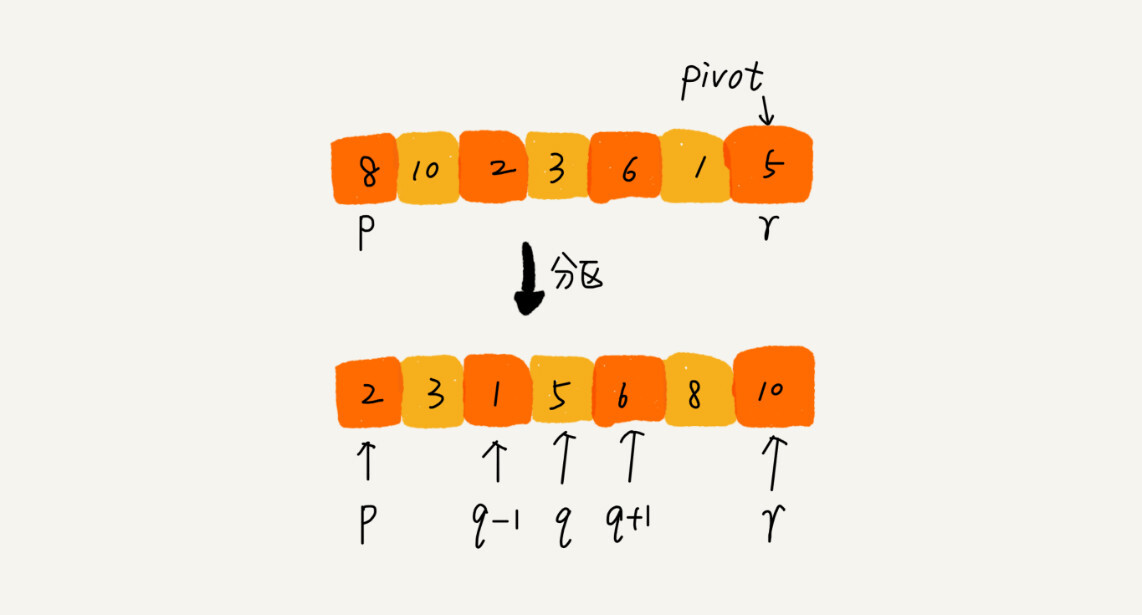
|
||||
|
||||
显然,这又是一个递归:
|
||||
|
||||
* 终止条件:区间 `[first, last)` 内不足 2 个元素
|
||||
* 递归公式:`quick_sort(first, last) = quick_sort(first, cut) + quick_sort(cut, last)`
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
template <typename IterT, typename T = typename std::iterator_traits<IterT>::value_type>
|
||||
void quick_sort(IterT first, IterT last) {
|
||||
if (std::distance(first, last) > 1) {
|
||||
IterT prev_last = std::prev(last);
|
||||
IterT cut = std::partition(first, prev_last, [prev_last](T v) { return v < *prev_last; });
|
||||
std::iter_swap(cut, prev_last);
|
||||
quick_sort(first, cut);
|
||||
quick_sort(cut, last);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> 一点优化(Liam Huang):通过将 `if` 改为 `while` 同时修改 `last` 迭代器的值,可以节省一半递归调用的开销。
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
template <typename IterT, typename T = typename std::iterator_traits<IterT>::value_type>
|
||||
void quick_sort(IterT first, IterT last) {
|
||||
while (std::distance(first, last) > 1) {
|
||||
IterT prev_last = std::prev(last);
|
||||
IterT cut = std::partition(first, prev_last, [prev_last](T v) { return v < *prev_last; });
|
||||
std::iter_swap(cut, prev_last);
|
||||
quick_sort(cut, last);
|
||||
last = cut;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果不要求空间复杂度,分区函数实现起来很容易。
|
||||
|
||||
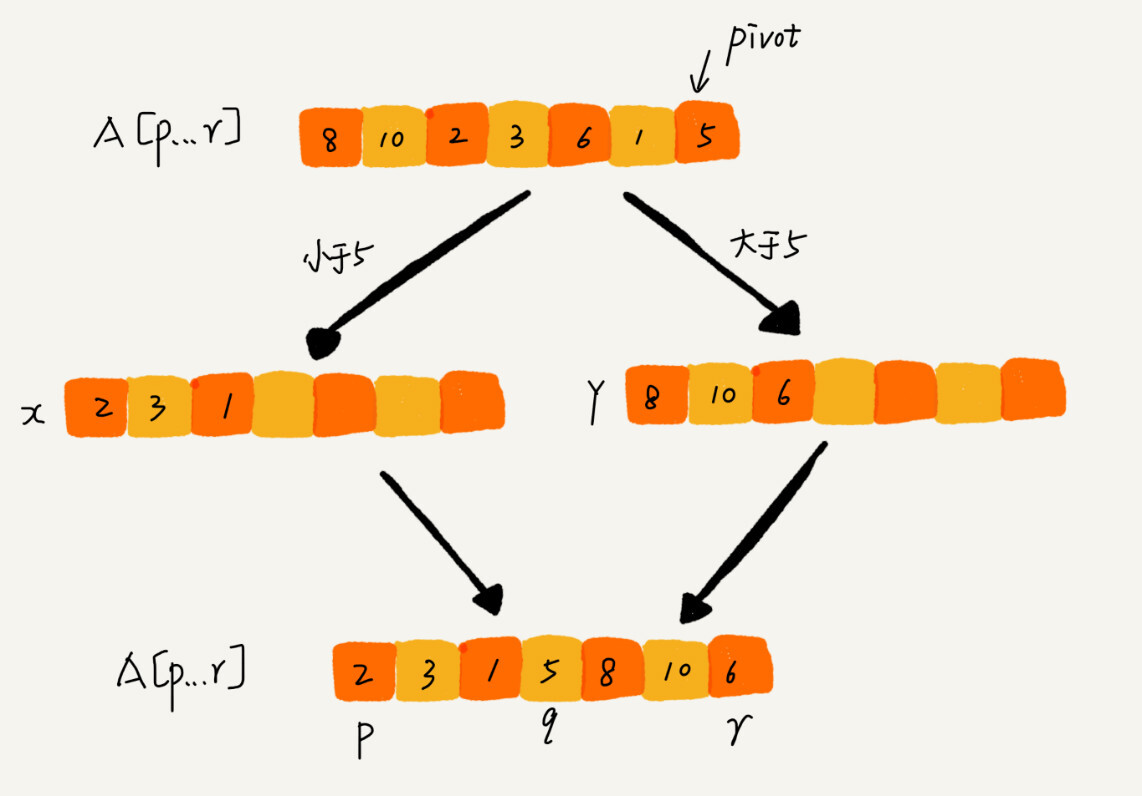
|
||||
|
||||
若要求原地分区,则不那么容易了。下面的实现实现了原地分区函数,并且能将所有相等的主元排在一起。
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
template <typename BidirIt,
|
||||
typename T = typename std::iterator_traits<BidirIt>::value_type,
|
||||
typename Compare = std::less<T>>
|
||||
std::pair<BidirIt, BidirIt> inplace_partition(BidirIt first,
|
||||
BidirIt last,
|
||||
const T& pivot,
|
||||
Compare comp = Compare()) {
|
||||
BidirIt last_less, last_greater, first_equal, last_equal;
|
||||
for (last_less = first, last_greater = first, first_equal = last;
|
||||
last_greater != first_equal; ) {
|
||||
if (comp(*last_greater, pivot)) {
|
||||
std::iter_swap(last_greater++, last_less++);
|
||||
} else if (comp(pivot, *last_greater)) {
|
||||
++last_greater;
|
||||
} else { // pivot == *last_greater
|
||||
std::iter_swap(last_greater, --first_equal);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
const auto cnt = std::distance(first_equal, last);
|
||||
std::swap_ranges(first_equal, last, last_less);
|
||||
first_equal = last_less;
|
||||
last_equal = first_equal + cnt;
|
||||
return {first_equal, last_equal};
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 算法分析
|
||||
|
||||
* 稳定性
|
||||
* 由于 `inplace_partition` 使用了大量 `std::iter_swap` 操作,所以不是稳定排序
|
||||
* 时间复杂度
|
||||
* 定义 $T(n)$ 表示问题规模为 $n$ 时算法的耗时,
|
||||
* 有递推公式:$T(n) = 2T(n/2) + n$(假定每次分割都是均衡分割)
|
||||
* 展开得 $T(n) = 2^{k}T(1) + k * n$
|
||||
* 考虑 $k$ 是递归深度,它的值是 $\log_2 n$,因此 $T(n) = n + n\log_2 n$
|
||||
* 因此,快速排序的时间复杂度为 $\Theta(n\log n)$
|
||||
* 空间复杂度
|
||||
* 一般来说,空间复杂度是 $\Theta(1)$,因此是原地排序算法
|
||||
|
||||
## 开篇问题
|
||||
|
||||
* 分区,看前半段元素数量
|
||||
* 前半段元素数量 < K,对后半段进行分区
|
||||
* 前半段元素数量 > K,对前半段进行分区
|
||||
* 前半段元素数量 = K,前半段末位元素即是所求
|
||||
0
notes/13_sorts/.gitkeep
Normal file
0
notes/13_sorts/.gitkeep
Normal file
77
notes/13_sorts/readme.md
Normal file
77
notes/13_sorts/readme.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,77 @@
|
||||
# 线性排序
|
||||
|
||||
## 开篇问题
|
||||
|
||||
如何按年龄给 100 万用户排序?
|
||||
|
||||
## 桶排序(Bucket Sort)
|
||||
|
||||
算法思想:
|
||||
|
||||
* 按待排序数据的 key 分有序桶
|
||||
* 桶内排序
|
||||
* 有序桶依次输出
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 算法分析
|
||||
|
||||
* 时间复杂度 $O(n)$
|
||||
* $n$ 个元素,分 $m$ 个有序桶,每个桶里平均 $k = n / m$ 个元素
|
||||
* 桶内快排,复杂度 $O(k \log k)$,$m$ 个桶一共 $O(n \log k)$
|
||||
* 当 $m$ 接近 $n$,例如当 $k = 4$ 时,这个复杂度近似 $O(n)$
|
||||
* 使用条件
|
||||
* 数据易于分如有序桶
|
||||
* 数据在各个有序桶之间分布均匀
|
||||
* 适合外部排序——数据不全部载入磁盘
|
||||
|
||||
## 计数排序(Counting Sort)
|
||||
|
||||
计数排序可以视作是桶排序的一个特殊情况:
|
||||
|
||||
* 数据的取值范围很小
|
||||
* 每个分桶内的元素 key 值都一样
|
||||
|
||||
此时,由于分桶内的元素 key 值都一样,所以桶内的排序操作可以省略,以及桶的编号本身就能记录桶内元素的值。因此,算法只需遍历一遍所有的数据,统计每个取值上有多少元素即可。这个过程时间复杂度是 $O(n)$。
|
||||
|
||||
* 假设待排序的数组 `A = {2, 5, 3, 0, 2, 3, 0, 3}`,我们有计数数组 `C = {2, 0, 2, 3, 0, 1}`
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,我们要对 `C` 进行计数操作,具体来说,对从下标为 1 的元素开始累加 `C[i] += C[i - 1]`。
|
||||
|
||||
* 计数累加 `C = {2, 2, 4, 7, 7, 8}`
|
||||
|
||||
此时,`C` 中的元素表示「小于等于下标的元素的个数」。接下来,我们从尾至头扫描待排序数组 `A`,将其中元素依次拷贝到输出数组 `R` 的相应位置。我们注意到,`A[7] = 3` 而 `C[3] == 4` 。这意味着,待排序的数组中,包括 3 本身在内,不超过 3 的元素共有 4 个。因此,我们可以将这个 3 放置在 `R[C[3] - 1]` 的位置,而后将 `C[3]` 的计数减一——这是由于待排序数组中未处理的部分,不超过 3 的元素现在只剩下 3 个了。如此遍历整个待排序数组 `A`,即可得到排序后的结果 `R`。
|
||||
|
||||
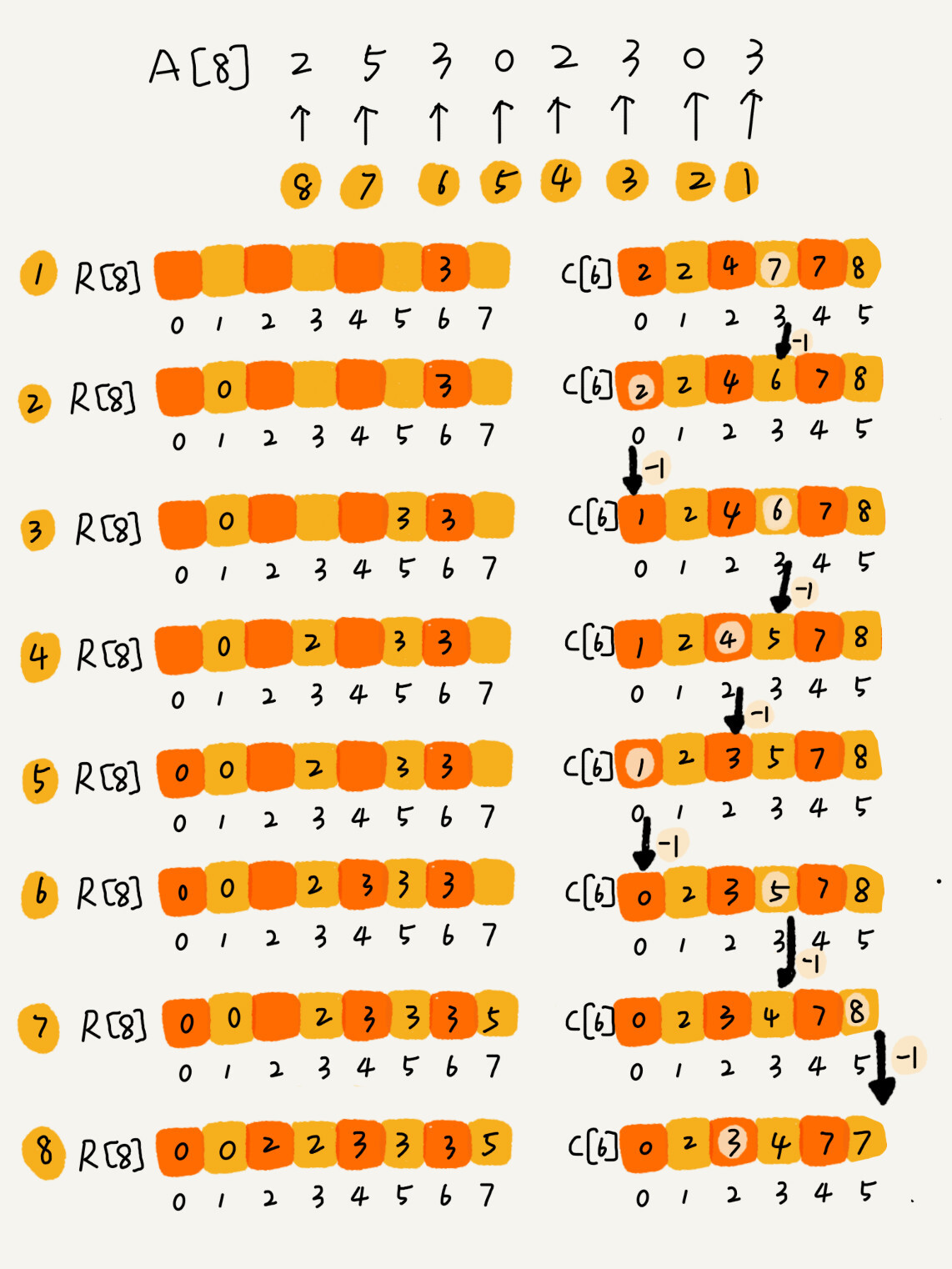
|
||||
|
||||
### 算法分析
|
||||
|
||||
* 时间复杂度
|
||||
* $n$ 个元素,最大值是 $k$,分 $k$ 个「桶」;时间复杂度 $O(n)$
|
||||
* 桶内计数累加;时间复杂度 $O(k)$
|
||||
* 摆放元素;时间复杂度 $O(n)$
|
||||
* 当 $k < n$ 时,总体时间复杂度是 $O(n)$
|
||||
* 使用条件
|
||||
* $k < n$
|
||||
* 待排序数据的 key 是非负整数
|
||||
|
||||
## 基数排序(Radix Sort)
|
||||
|
||||
基数排序适用于等长数据的排序。对于不等长数据,可以在较短的数据后面做 padding,使得数据等长。
|
||||
|
||||
* 先就 least significant digit 进行稳定排序——通常可以用桶排序或者计数排序;时间复杂度 $O(n)$
|
||||
* 而后依次向 greatest significant digit 移动,进行稳定排序
|
||||
|
||||
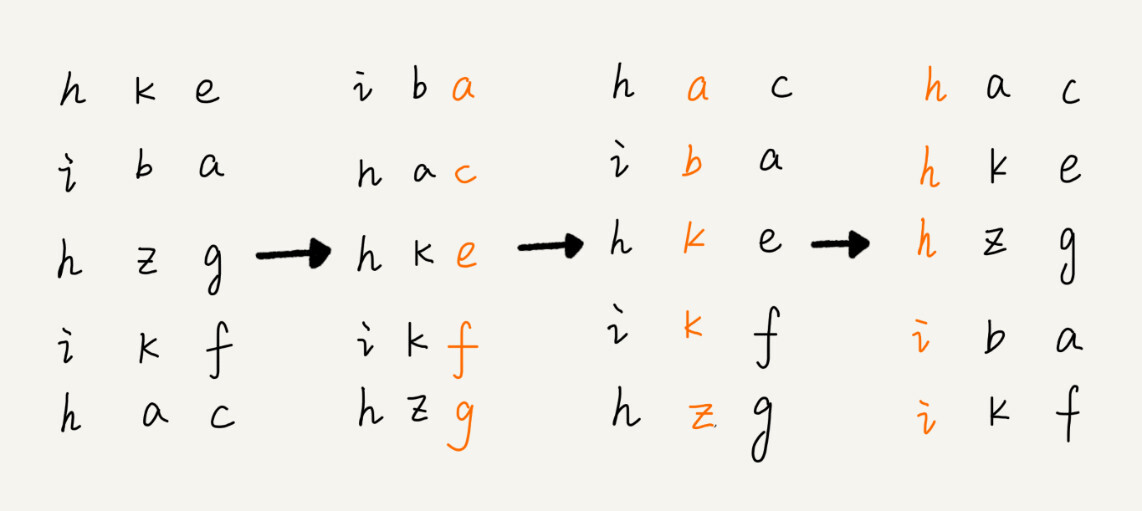
|
||||
|
||||
### 算法分析
|
||||
|
||||
* 时间复杂度
|
||||
* 对每一位的排序时间复杂度是 $O(n)$
|
||||
* 总共 $k$ 位,因此总的时间复杂度是 $O(kn)$;考虑到 $k$ 是常数,因此总的时间复杂度是 $O(n)$
|
||||
* 使用条件
|
||||
* 等长数据
|
||||
|
||||
## 解答开篇
|
||||
|
||||
桶排序。
|
||||
0
notes/14_sorts/.gitkeep
Normal file
0
notes/14_sorts/.gitkeep
Normal file
10
notes/14_sorts/readme.md
Normal file
10
notes/14_sorts/readme.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,10 @@
|
||||
# 排序优化
|
||||
|
||||
## 如何取舍排序算法?
|
||||
|
||||
* 排序规模小 —— $O(n^2)$ 的算法(通常是插排)
|
||||
* 排序规模大 —— $O(n\log n)$ 的算法(通常不用归并排序)
|
||||
|
||||
## 如何优化快速排序?
|
||||
|
||||
参考:[谈谈内省式排序算法](https://liam.page/2018/08/29/introspective-sort/)
|
||||
0
notes/15_bsearch/.gitkeep
Normal file
0
notes/15_bsearch/.gitkeep
Normal file
23
notes/15_bsearch/readme.md
Normal file
23
notes/15_bsearch/readme.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
|
||||
# 二分查找(上)
|
||||
|
||||
## 算法描述
|
||||
|
||||
二分查找(Binary Search)也叫折半查找,是针对有序数据集合的查找算法。其描述十分简单:
|
||||
|
||||
* 折半取中,判断元素与目标元素的大小关系
|
||||
* 小于——往前继续折半
|
||||
* 大于——往后继续折半
|
||||
* 等于——返回
|
||||
|
||||
关于它的复杂度分析,参见[谈谈基于比较的排序算法的复杂度下界](https://liam.page/2018/08/28/lower-bound-of-comparation-based-sort-algorithm/)中的相关信息。它的复杂度是 $O(\log n)$。
|
||||
|
||||
## $O(\log n)$ 的惊人之处
|
||||
|
||||
在 42 亿个数据中用二分查找一个数据,最多需要比较 32 次。
|
||||
|
||||
## 适用场景
|
||||
|
||||
* 依赖顺序表结构
|
||||
* 数据本身必须有序
|
||||
* 数据量相对比较元素的开销要足够大——不然遍历即可
|
||||
* 数据量相对内存空间不能太大——不然顺序表装不下
|
||||
0
notes/16_bsearch/.gitkeep
Normal file
0
notes/16_bsearch/.gitkeep
Normal file
100
notes/16_bsearch/readme.md
Normal file
100
notes/16_bsearch/readme.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,100 @@
|
||||
# 二分查找(下)
|
||||
|
||||
本节课讨论二分的各种变体。实际上在针对上一节的代码中,已经实现了两个变体。本次实现四个变体:
|
||||
|
||||
* 第一个等于给定值的元素
|
||||
* 最后一个等于给定值的元素
|
||||
* 第一个不小于给定值的元素
|
||||
* 最后一个不大于给定值的元素
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Created by Liam Huang (Liam0205) on 2018/10/26.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef BSEARCH_BSEARCH_VARIENTS_HPP_
|
||||
#define BSEARCH_BSEARCH_VARIENTS_HPP_
|
||||
|
||||
#include <iterator>
|
||||
#include <functional>
|
||||
|
||||
enum class BsearchPolicy { UNSPECIFIED, FIRST, LAST, FIRST_NOT_LESS, LAST_NOT_GREATER };
|
||||
|
||||
// Liam Huang: The algorithm works right with iterators that meet the ForwardIterator requirement,
|
||||
// but with a bad time complexity. For better performance, iterators should meet
|
||||
// the RandomAccessIterator requirement.
|
||||
template <typename IterT,
|
||||
typename ValueT = typename std::iterator_traits<IterT>::value_type,
|
||||
typename Compare>
|
||||
IterT bsearch(IterT first,
|
||||
IterT last,
|
||||
ValueT target,
|
||||
Compare comp,
|
||||
BsearchPolicy policy = BsearchPolicy::UNSPECIFIED) {
|
||||
IterT result = last;
|
||||
while (std::distance(first, last) > 0) {
|
||||
IterT mid = first + std::distance(first, last) / 2;
|
||||
if (policy == BsearchPolicy::FIRST_NOT_LESS) {
|
||||
if (!comp(*mid, target)) {
|
||||
if (mid == first or comp(*(mid - 1), target)) {
|
||||
result = mid;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
last = mid;
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
first = mid + 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if (policy == BsearchPolicy::LAST_NOT_GREATER) {
|
||||
if (comp(target, *mid)) {
|
||||
last = mid;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if (std::distance(mid, last) == 1 or comp(target, *(mid + 1))) {
|
||||
result = mid;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
first = mid + 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else { // policy == UNSPECIFIED or FIRST or LAST
|
||||
if (comp(*mid, target)) {
|
||||
first = mid + 1;
|
||||
} else if (comp(target, *mid)) {
|
||||
last = mid;
|
||||
} else { // equal
|
||||
if (policy == BsearchPolicy::FIRST) {
|
||||
if (mid == first or comp(*(mid - 1), *mid)) {
|
||||
result = mid;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
last = mid;
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if (policy == BsearchPolicy::LAST) {
|
||||
if (std::distance(mid, last) == 1 or comp(*mid, *(mid + 1))) {
|
||||
result = mid;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
first = mid + 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
result = mid;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return result;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename IterT,
|
||||
typename ValueT = typename std::iterator_traits<IterT>::value_type,
|
||||
typename Compare = std::less<ValueT>>
|
||||
IterT bsearch(IterT first,
|
||||
IterT last,
|
||||
ValueT target,
|
||||
BsearchPolicy policy = BsearchPolicy::UNSPECIFIED) {
|
||||
return bsearch(first, last, target, Compare(), policy);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#endif // BSEARCH_BSEARCH_VARIENTS_HPP_
|
||||
```
|
||||
0
notes/17_skiplist/.gitkeep
Normal file
0
notes/17_skiplist/.gitkeep
Normal file
43
notes/17_skiplist/readme.md
Normal file
43
notes/17_skiplist/readme.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
|
||||
# 跳表(Skip List)
|
||||
|
||||
支持快速地:
|
||||
|
||||
* 插入
|
||||
* 删除
|
||||
* 查找
|
||||
|
||||
某些情况下,跳表甚至可以替代红黑树(Red-Black tree)。Redis 当中的有序集合(Sorted Set)是用跳表实现的。
|
||||
|
||||
## 跳表的结构
|
||||
|
||||
跳表是对链表的改进。对于单链表来说,即使内容是有序的,查找具体某个元素的时间复杂度也要达到 $O(n)$。对于二分查找来说,由于链表不支持随机访问,根据 `first` 和 `last` 确定 `cut` 时,必须沿着链表依次迭代 `std::distance(first, last) / 2` 步;特别地,计算 `std::(first, last)` 本身,就必须沿着链表迭代才行。此时,二分查找的效率甚至退化到了 $O(n \log n)$,甚至还不如顺序遍历。
|
||||
|
||||
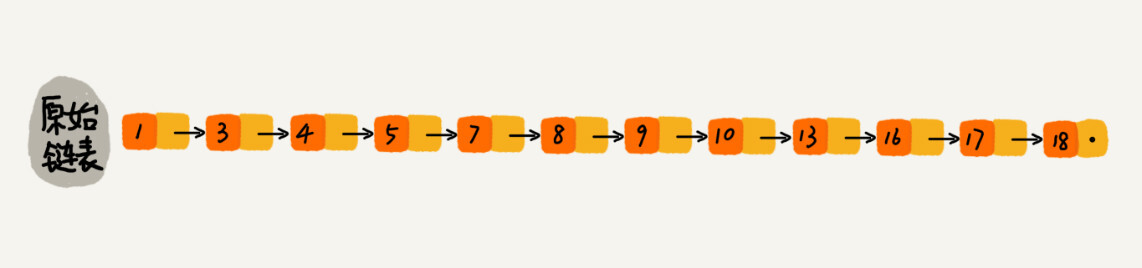
|
||||
|
||||
跳表的核心思想是用空间换时间,构建足够多级数的索引,来缩短查找具体值的时间开销。
|
||||
|
||||
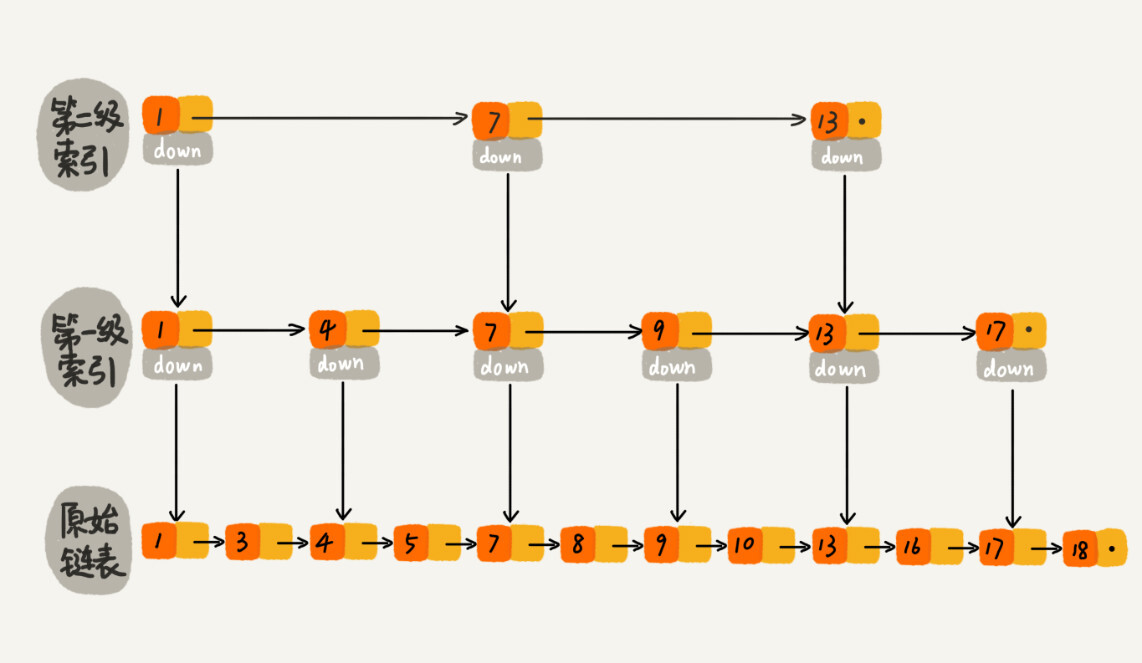
|
||||
|
||||
例如对于一个具有 64 个有序元素的五级跳表,查找起来的过程大约如下图所示。
|
||||
|
||||
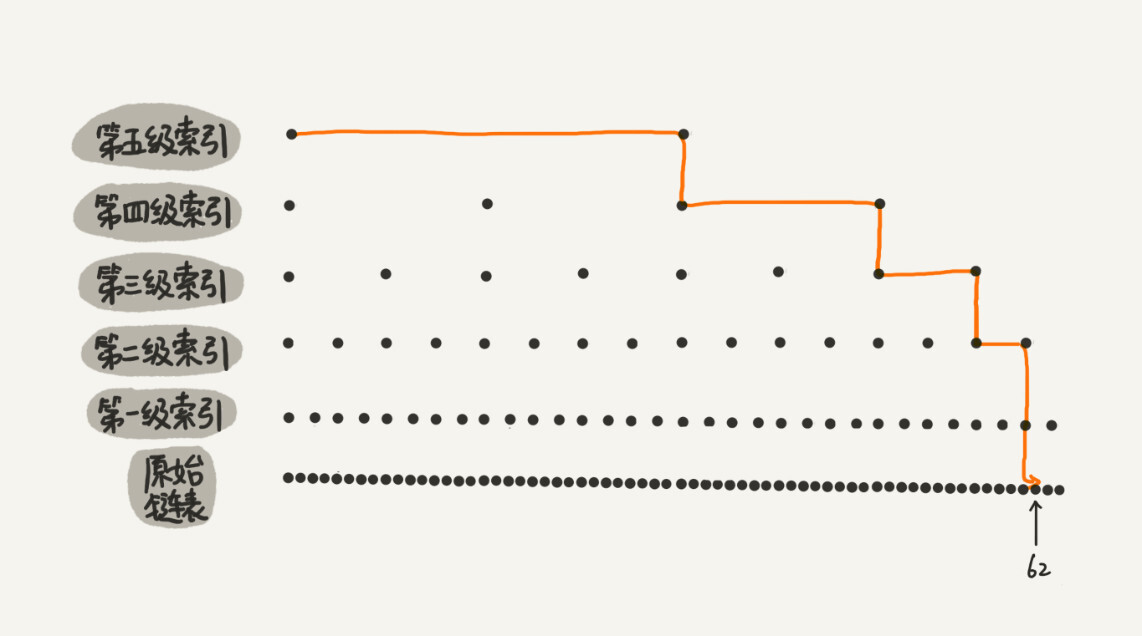
|
||||
|
||||
## 复杂度分析
|
||||
|
||||
对于一个每一级索引的跨度是下一级索引 $k$ 倍的跳表,每一次 `down` 操作,相当于将搜索范围缩小到「剩余的可能性的 $1 / k$」。因此,查找具体某个元素的时间复杂度大约需要 $\lfloor \log_k n\rfloor + 1$ 次操作;也就是说时间复杂度是 $O(\log n)$。
|
||||
|
||||
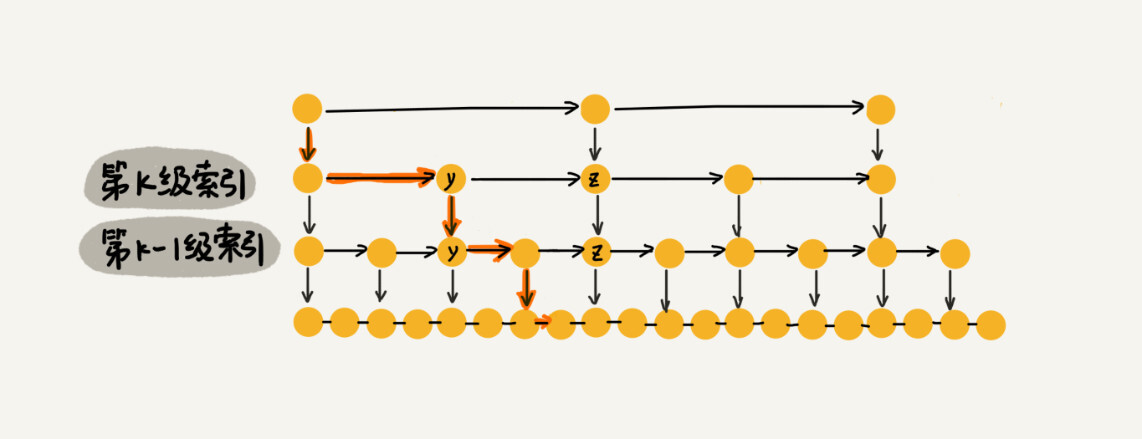
|
||||
|
||||
前面说了,跳表是一种用空间换时间的数据结构。因此它的空间复杂度一定不小。我们考虑原链表有 $n$ 个元素,那么第一级索引就有 $n / k$ 个元素,剩余的索引依次有 $n / k^2$, $n / k^3$, ..., $1$ 个元素。总共的元素个数是一个等比数列求和问题,它的值是 $\frac{n - 1}{k - 1}$。可见,不论 $k$ 是多少,跳表的空间复杂度都是 $O(n)$;但随着 $k$ 的增加,实际需要的额外节点数会下降。
|
||||
|
||||
## 高效地插入和删除
|
||||
|
||||
对于链表来说,插入或删除一个给定结点的时间复杂度是 $O(1)$。因此,对于跳表来说,插入或删除某个结点,其时间复杂度完全依赖于查找这类结点的耗时。而我们知道,在跳表中查找某个元素的时间复杂度是 $O(\log n)$。因此,在跳表中插入或删除某个结点的时间复杂度是 $O(\log n)$。
|
||||
|
||||
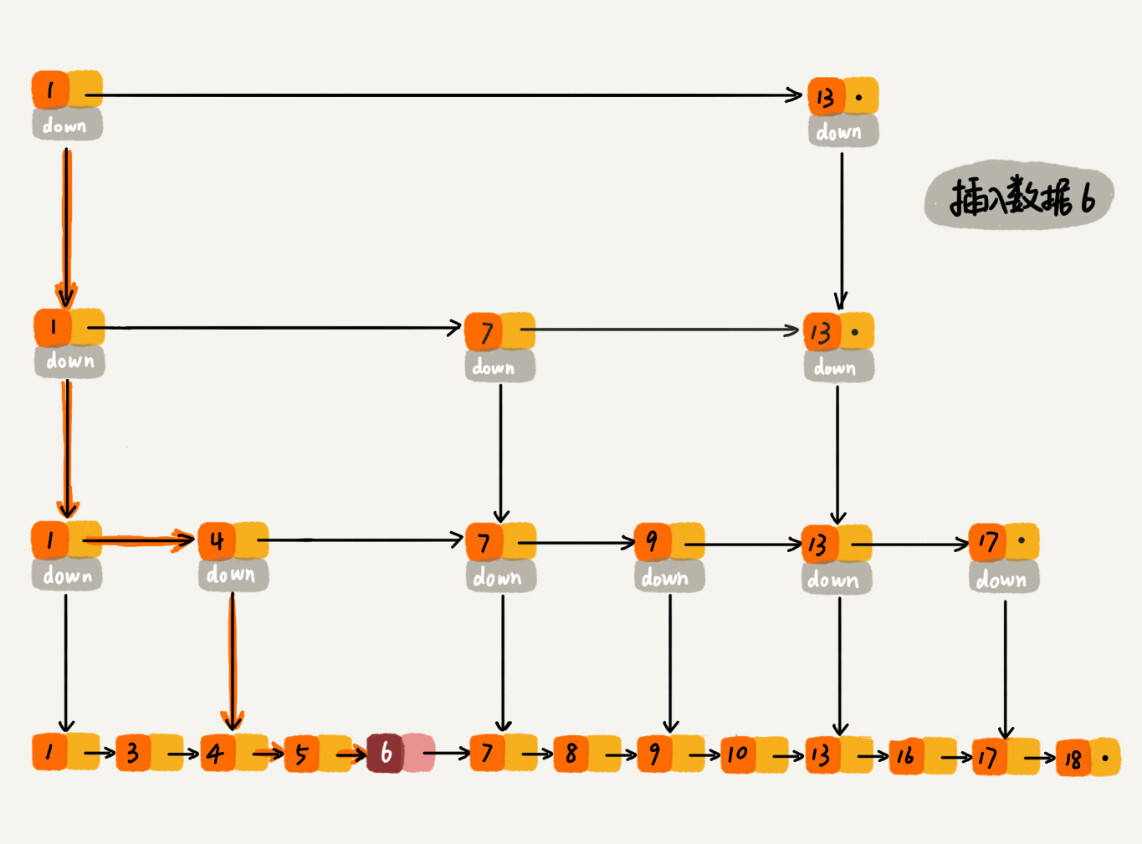
|
||||
|
||||
## 跳表索引的动态更新
|
||||
|
||||
为了维护跳表的结构,在不断插入数据的过程中,有必要动态维护跳表的索引结构。一般来说,可以采用随机层级法。具体来说是引入一个输出整数的随机函数。当随机函数输出 $K$,则更新从第 $1$ 级至第 $K$ 级的索引。为了保证索引结构和数据规模大小的匹配,一般采用二项分布的随机函数。
|
||||
|
||||
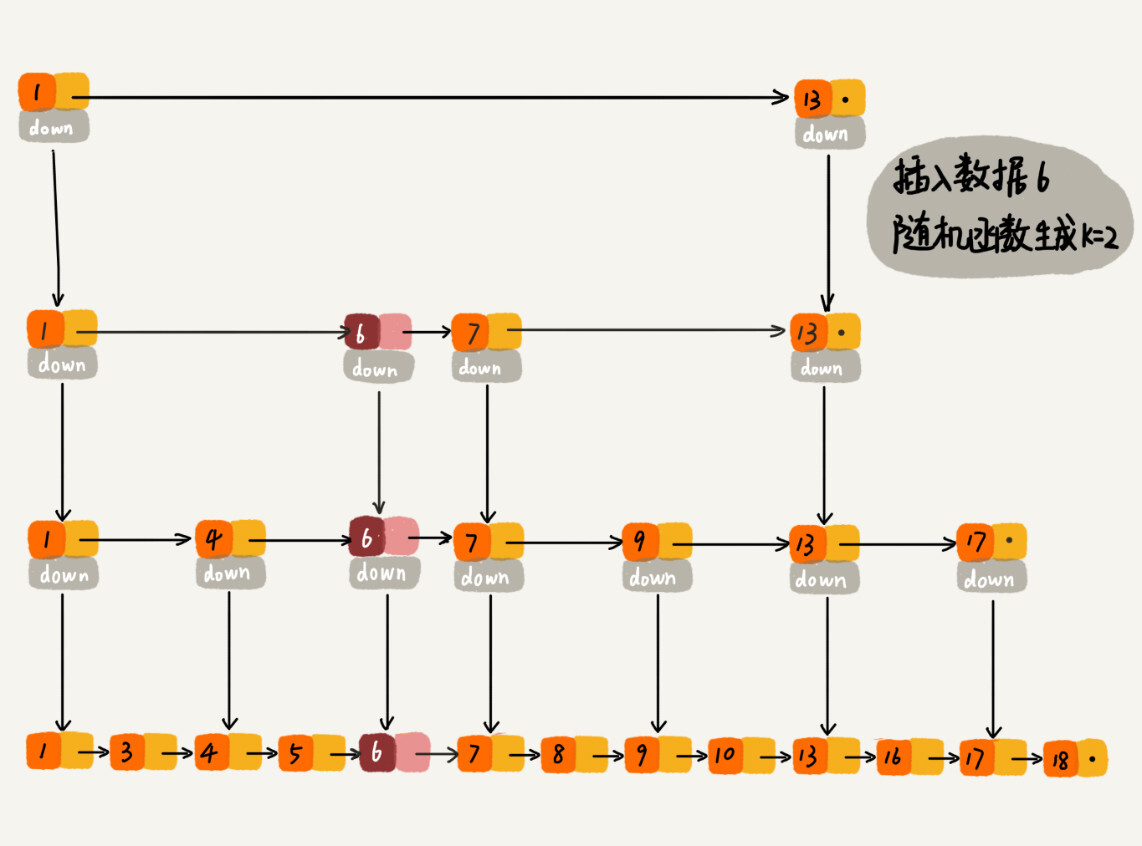
|
||||
47
php/12_sort/quicksort.php
Normal file
47
php/12_sort/quicksort.php
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
|
||||
<?php
|
||||
|
||||
function quickSort(array &$a)
|
||||
{
|
||||
$n = count($a);
|
||||
|
||||
quickSortInternally($a, 0, $n-1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
function quickSortInternally(array &$a, int $l, int $r)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if ($l >= $r) return;
|
||||
|
||||
$q = partition($a, $l, $r);
|
||||
quickSortInternally($a, $l, $q-1);
|
||||
quickSortInternally($a, $q+1, $r);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
function partition(&$a, $l, $r): int
|
||||
{
|
||||
$pivot = $a[$r];
|
||||
$i = $l;
|
||||
|
||||
for ($j = $l; $j < $r; ++$j) {
|
||||
if ($a[$j] < $pivot) {
|
||||
[$a[$j], $a[$i]] = [$a[$i], $a[$j]];
|
||||
++$i;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
[$a[$r], $a[$i]] = [$a[$i], $a[$r]];
|
||||
|
||||
return $i;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
$a1 = [1,4,6,2,3,5,4];
|
||||
$a2 = [2, 2, 2, 2];
|
||||
$a3 = [4, 3, 2, 1];
|
||||
$a4 = [5, -1, 9, 3, 7, 8, 3, -2, 9];
|
||||
quickSort($a1);
|
||||
print_r($a1);
|
||||
quickSort($a2);
|
||||
print_r($a2);
|
||||
quickSort($a3);
|
||||
print_r($a3);
|
||||
quickSort($a4);
|
||||
print_r($a4);
|
||||
BIN
python/.vs/slnx.sqlite
Normal file
BIN
python/.vs/slnx.sqlite
Normal file
Binary file not shown.
75
python/08_stack/simple_browser.py
Normal file
75
python/08_stack/simple_browser.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,75 @@
|
||||
"""
|
||||
a simple browser realize
|
||||
Author: zhenchao.zhu
|
||||
解答:我们使用两个栈,X 和 Y,我们把首次浏览的页面依次压入栈 X,当点击后退按钮时,再依次从栈 X 中出栈,
|
||||
并将出栈的数据依次放入栈 Y。当我们点击前进按钮时,我们依次从栈 Y 中取出数据,放入栈 X 中。
|
||||
当栈 X 中没有数据时,那就说明没有页面可以继续后退浏览了。当栈 Y 中没有数据,
|
||||
那就说明没有页面可以点击前进按钮浏览了。
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
# 引用当前文件夹下的single_linked_list
|
||||
sys.path.append('linked_stack.py')
|
||||
from linked_stack import LinkedStack
|
||||
#from .linked_stack import LinkedStack
|
||||
|
||||
class NewLinkedStack(LinkedStack):
|
||||
|
||||
def is_empty(self):
|
||||
return not self._top
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Browser():
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self):
|
||||
self.forward_stack = NewLinkedStack()
|
||||
self.back_stack = NewLinkedStack()
|
||||
|
||||
def can_forward(self):
|
||||
if self.back_stack.is_empty():
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
return True
|
||||
|
||||
def can_back(self):
|
||||
if self.forward_stack.is_empty():
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
return True
|
||||
|
||||
def open(self, url):
|
||||
print("Open new url %s" % url, end="\n")
|
||||
self.forward_stack.push(url)
|
||||
|
||||
def back(self):
|
||||
if self.forward_stack.is_empty():
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
top = self.forward_stack.pop()
|
||||
self.back_stack.push(top)
|
||||
print("back to %s" % top, end="\n")
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self):
|
||||
if self.back_stack.is_empty():
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
top = self.back_stack.pop()
|
||||
self.forward_stack.push(top)
|
||||
print("forward to %s" % top, end="\n")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == '__main__':
|
||||
|
||||
browser = Browser()
|
||||
browser.open('a')
|
||||
browser.open('b')
|
||||
browser.open('c')
|
||||
if browser.can_back():
|
||||
browser.back()
|
||||
|
||||
if browser.can_forward():
|
||||
browser.forward()
|
||||
|
||||
browser.back()
|
||||
browser.back()
|
||||
browser.back()
|
||||
91
python/17_skiplist/skip_list.py
Normal file
91
python/17_skiplist/skip_list.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,91 @@
|
||||
"""
|
||||
An implementation of skip list.
|
||||
The list stores positive integers without duplicates.
|
||||
|
||||
跳表的一种实现方法。
|
||||
跳表中储存的是正整数,并且储存的是不重复的。
|
||||
|
||||
Author: Wenru
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
from typing import Optional
|
||||
import random
|
||||
|
||||
class ListNode:
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, data: Optional[int] = None):
|
||||
self._data = data
|
||||
self._forwards = [] # Forward pointers
|
||||
|
||||
class SkipList:
|
||||
|
||||
_MAX_LEVEL = 16
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self):
|
||||
self._level_count = 1
|
||||
self._head = ListNode()
|
||||
self._head._forwards = [None] * type(self)._MAX_LEVEL
|
||||
|
||||
def find(self, value: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
|
||||
p = self._head
|
||||
for i in range(self._level_count - 1, -1, -1): # Move down a level
|
||||
while p._forwards[i] and p._forwards[i]._data < value:
|
||||
p = p._forwards[i] # Move along level
|
||||
|
||||
return p._forwards[0] if p._forwards[0] and p._forwards[0]._data == value else None
|
||||
|
||||
def insert(self, value: int):
|
||||
level = self._random_level()
|
||||
if self._level_count < level: self._level_count = level
|
||||
new_node = ListNode(value)
|
||||
new_node._forwards = [None] * level
|
||||
update = [self._head] * level # update is like a list of prevs
|
||||
|
||||
p = self._head
|
||||
for i in range(level - 1, -1, -1):
|
||||
while p._forwards[i] and p._forwards[i]._data < value:
|
||||
p = p._forwards[i]
|
||||
|
||||
update[i] = p # Found a prev
|
||||
|
||||
for i in range(level):
|
||||
new_node._forwards[i] = update[i]._forwards[i] # new_node.next = prev.next
|
||||
update[i]._forwards[i] = new_node # prev.next = new_node
|
||||
|
||||
def delete(self, value):
|
||||
update = [None] * self._level_count
|
||||
p = self._head
|
||||
for i in range(self._level_count - 1, -1, -1):
|
||||
while p._forwards[i] and p._forwards[i]._data < value:
|
||||
p = p._forwards[i]
|
||||
update[i] = p
|
||||
|
||||
if p._forwards[0] and p._forwards[0]._data == value:
|
||||
for i in range(self._level_count - 1, -1, -1):
|
||||
if update[i]._forwards[i] and update[i]._forwards[i]._data == value:
|
||||
update[i]._forwards[i] = update[i]._forwards[i]._forwards[i] # Similar to prev.next = prev.next.next
|
||||
|
||||
def _random_level(self, p: float = 0.5) -> int:
|
||||
level = 1
|
||||
while random.random() < p and level < type(self)._MAX_LEVEL:
|
||||
level += 1
|
||||
return level
|
||||
|
||||
def __repr__(self) -> str:
|
||||
values = []
|
||||
p = self._head
|
||||
while p._forwards[0]:
|
||||
values.append(str(p._forwards[0]._data))
|
||||
p = p._forwards[0]
|
||||
return "->".join(values)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
l = SkipList()
|
||||
for i in range(10):
|
||||
l.insert(i)
|
||||
print(l)
|
||||
p = l.find(7)
|
||||
print(p._data)
|
||||
l.delete(3)
|
||||
print(l)
|
||||
18
scala/15_bsearch/BSearch.scala
Normal file
18
scala/15_bsearch/BSearch.scala
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
|
||||
object BSearch {
|
||||
def search(nums: Array[Int], target: Int): Int = {
|
||||
var low = 0
|
||||
var high = nums.length - 1
|
||||
while(low <= high){
|
||||
val mid = low + ((high - low) >> 2)
|
||||
if(nums(mid) > target){
|
||||
high = mid - 1
|
||||
} else if (nums(mid) < target){
|
||||
low = mid + 1
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
return mid
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
20
scala/15_bsearch/BSearchRecursive.scala
Normal file
20
scala/15_bsearch/BSearchRecursive.scala
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,20 @@
|
||||
object BSearchRecursive {
|
||||
def search(nums: Array[Int], target: Int): Int = {
|
||||
return searchInternal(nums, target, 0, nums.length - 1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
def searchInternal(nums:Array[Int], target: Int, low: Int, high: Int): Int = {
|
||||
if(low <= high){
|
||||
val mid = low + ((high - low) >> 2)
|
||||
if(nums(mid) > target){
|
||||
searchInternal(nums, target, low, mid - 1)
|
||||
} else if (nums(mid) < target){
|
||||
searchInternal(nums, target, mid + 1, high)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
return mid
|
||||
}
|
||||
}else{
|
||||
return -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
128
swift/06_linkedlist/SinglyLinkedList.swift
Normal file
128
swift/06_linkedlist/SinglyLinkedList.swift
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,128 @@
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Created by Jiandan on 2018/10/12.
|
||||
// Copyright © 2018 Jiandan. All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
|
||||
import Foundation
|
||||
|
||||
class Node<T> {
|
||||
var value: T?
|
||||
var next: Node?
|
||||
|
||||
init(){}
|
||||
|
||||
init(value: T) {
|
||||
self.value = value
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/// 单链表
|
||||
/// 实现插入、删除、查找操作
|
||||
class List<Element: Equatable> {
|
||||
private var dummy = Node<Element>() // 哨兵结点,不存储数据
|
||||
var size: Int {
|
||||
var num = 0
|
||||
var tmpNode = dummy.next
|
||||
while tmpNode != nil {
|
||||
num += 1
|
||||
tmpNode = tmpNode!.next
|
||||
}
|
||||
return num
|
||||
}
|
||||
var isEmpty: Bool { return size > 0 }
|
||||
|
||||
/// find node with value
|
||||
func node(with value: Element) -> Node<Element>? {
|
||||
var node = dummy.next
|
||||
while node != nil {
|
||||
if node!.value == value {
|
||||
return node
|
||||
}
|
||||
node = node!.next
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 约定:链表的 index 从 1 开始
|
||||
func node(at index: Int) -> Node<Element>? {
|
||||
var num = 1
|
||||
var node = dummy.next
|
||||
while node != nil {
|
||||
if num == index {
|
||||
return node
|
||||
}
|
||||
node = node!.next
|
||||
num += 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func insertToHead(value: Element) {
|
||||
let newNode = Node(value: value)
|
||||
return insertToHead(node: newNode)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func insertToHead(node: Node<Element>) {
|
||||
node.next = dummy.next
|
||||
dummy.next = node
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func insert(after node: Node<Element>, newValue: Element) {
|
||||
let newNode = Node(value: newValue)
|
||||
return insert(after: node, newNode: newNode)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func insert(after node: Node<Element>, newNode: Node<Element>) {
|
||||
newNode.next = node.next
|
||||
node.next = newNode
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func insert(before node: Node<Element>, newValue: Element) {
|
||||
let newNode = Node(value: newValue)
|
||||
return insert(before: node, newNode: newNode)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func insert(before node: Node<Element>, newNode: Node<Element>) {
|
||||
var lastNode = dummy
|
||||
var tmpNode = dummy.next
|
||||
|
||||
while tmpNode != nil {
|
||||
if tmpNode === node {
|
||||
newNode.next = tmpNode
|
||||
lastNode.next = newNode
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
lastNode = tmpNode!
|
||||
tmpNode = tmpNode!.next
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func delete(node: Node<Element>) {
|
||||
var lastNode = dummy
|
||||
var tmpNode = dummy.next
|
||||
|
||||
while tmpNode != nil {
|
||||
if tmpNode === node {
|
||||
lastNode.next = tmpNode!.next
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
lastNode = tmpNode!
|
||||
tmpNode = tmpNode!.next
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
/// 删除首个 value 符合要求的结点
|
||||
func delete(value: Element) {
|
||||
var lastNode = dummy
|
||||
var tmpNode = dummy.next
|
||||
while tmpNode != nil {
|
||||
if tmpNode!.value == value {
|
||||
lastNode.next = tmpNode!.next
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
lastNode = tmpNode!
|
||||
tmpNode = tmpNode!.next
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
111
swift/07_linkedlist/LinkedListAlgo.swift
Normal file
111
swift/07_linkedlist/LinkedListAlgo.swift
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,111 @@
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Created by Jiandan on 2018/10/13.
|
||||
// Copyright (c) 2018 Jiandan. All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 1) 单链表反转
|
||||
* 2) 链表中环的检测
|
||||
* 3) 两个有序的链表合并
|
||||
* 4) 删除链表倒数第n个结点
|
||||
* 5) 求链表的中间结点
|
||||
*/
|
||||
import Foundation
|
||||
/// 单链表反转
|
||||
func reverseSinglyLinkedList<Element>(head: Node<Element>) -> Node<Element>? {
|
||||
var reverseHead: Node<Element>?, currentNode: Node<Element>?, prevNode: Node<Element>?
|
||||
currentNode = head
|
||||
while currentNode != nil {
|
||||
let nextNode = currentNode!.next
|
||||
if nextNode == nil {
|
||||
reverseHead = currentNode
|
||||
}
|
||||
currentNode!.next = prevNode
|
||||
prevNode = currentNode
|
||||
currentNode = nextNode
|
||||
}
|
||||
return reverseHead
|
||||
}
|
||||
/// 检测环
|
||||
func hasCircle<Element>(head: Node<Element>) -> Bool {
|
||||
var fast = head.next
|
||||
var slow: Node<Element>? = head
|
||||
while fast != nil {
|
||||
if fast === slow {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
fast = fast!.next?.next
|
||||
slow = slow!.next
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
/// 两个有序的链表合并
|
||||
func mergeSortedLists<Element: Comparable>(headA: Node<Element>?, headB: Node<Element>?) -> Node<Element>? {
|
||||
guard let headA = headA else {
|
||||
return headB
|
||||
}
|
||||
guard let headB = headB else {
|
||||
return headA
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var head: Node<Element>?, tail: Node<Element>?
|
||||
var nodeA: Node<Element>? = headA, nodeB: Node<Element>? = headB
|
||||
if nodeA!.value! < nodeB!.value! {
|
||||
head = nodeA
|
||||
nodeA = nodeA!.next
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
head = nodeB
|
||||
nodeB = nodeB!.next
|
||||
}
|
||||
tail = head
|
||||
|
||||
while nodeA != nil, nodeB != nil {
|
||||
if nodeA!.value! < nodeB!.value! {
|
||||
tail!.next = nodeA
|
||||
nodeA = nodeA!.next
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
tail!.next = nodeB
|
||||
nodeB = nodeB!.next
|
||||
}
|
||||
tail = tail!.next
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if nodeA != nil {
|
||||
tail?.next = nodeA
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
tail?.next = nodeB
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return head
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/// 删除倒数第n个结点
|
||||
func deleteNode<Element>(at lastNum: Int, in head: Node<Element>) {
|
||||
var slow: Node<Element>? = head
|
||||
var fast: Node<Element>? = head
|
||||
var num = 1
|
||||
while fast != nil, num < lastNum {
|
||||
fast = fast!.next
|
||||
num += 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var prevNode: Node<Element>?
|
||||
while fast != nil {
|
||||
prevNode = slow
|
||||
fast = fast!.next
|
||||
slow = slow!.next
|
||||
}
|
||||
prevNode?.next = slow?.next
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/// 求链表的中间结点
|
||||
func halfNode<Element>(in head: Node<Element>) -> Node<Element>? {
|
||||
var slow: Node<Element>? = head
|
||||
var fast: Node<Element>? = head
|
||||
|
||||
while fast?.next != nil, fast?.next?.next != nil {
|
||||
fast = fast!.next?.next
|
||||
slow = slow!.next
|
||||
}
|
||||
return slow
|
||||
}
|
||||
27
swift/08_stack/Browser.swift
Normal file
27
swift/08_stack/Browser.swift
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Created by Jiandan on 2018/10/12.
|
||||
// Copyright (c) 2018 Jiandan. All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
|
||||
import Foundation
|
||||
|
||||
struct Page {
|
||||
/// 存储前进 url
|
||||
private var forwardArray = [String]()
|
||||
/// 存储后退 url
|
||||
private var backArray = [String]()
|
||||
|
||||
var currentURL: String? { return forwardArray.last }
|
||||
|
||||
init(url: String) {
|
||||
forwardArray.append(url)
|
||||
}
|
||||
/// 前进
|
||||
mutating func goForward(url: String) {
|
||||
forwardArray.append(url)
|
||||
}
|
||||
/// 后退
|
||||
mutating func goBack() {
|
||||
backArray.append(forwardArray.popLast()!)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
27
swift/08_stack/BrowserDemo.swift
Normal file
27
swift/08_stack/BrowserDemo.swift
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Created by Jiandan on 2018/10/12.
|
||||
// Copyright (c) 2018 Jiandan. All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
|
||||
import Foundation
|
||||
|
||||
struct Page {
|
||||
/// 存储前进 url
|
||||
private var forwardArray = [String]()
|
||||
/// 存储后退 url
|
||||
private var backArray = [String]()
|
||||
|
||||
var currentURL: String { return forwardArray.last! }
|
||||
|
||||
init(url: String) {
|
||||
forwardArray.append(url)
|
||||
}
|
||||
/// 前进
|
||||
mutating func goForward(url: String) {
|
||||
forwardArray.append(url)
|
||||
}
|
||||
/// 后退
|
||||
mutating func goBack() {
|
||||
backArray.append(forwardArray.popLast()!)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
21
swift/08_stack/Stack.swift
Normal file
21
swift/08_stack/Stack.swift
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Created by Jiandan on 2018/10/12.
|
||||
// Copyright (c) 2018 Jiandan. All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
|
||||
import Foundation
|
||||
|
||||
protocol Stack {
|
||||
/// 持有的数据类型
|
||||
associatedtype Element
|
||||
/// 是否为空
|
||||
var isEmpty: Bool { get }
|
||||
/// 队列大小
|
||||
var size: Int { get }
|
||||
/// 返回队列头部元素
|
||||
var peek: Element? { get }
|
||||
/// 入栈
|
||||
mutating func push(newElement: Element) -> Bool
|
||||
/// 出栈
|
||||
mutating func pop() -> Element?
|
||||
}
|
||||
37
swift/08_stack/StackBasedOnLinkedList.swift
Normal file
37
swift/08_stack/StackBasedOnLinkedList.swift
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Created by Jiandan on 2018/10/12.
|
||||
// Copyright (c) 2018 Jiandan. All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
|
||||
import Foundation
|
||||
|
||||
struct StackBasedOnLinkedList<Element>: Stack {
|
||||
private var head = Node<Element>() // 哨兵结点,不存储内容
|
||||
|
||||
// MARK: Protocol: Stack
|
||||
|
||||
var isEmpty: Bool { return head.next == nil }
|
||||
|
||||
var size: Int {
|
||||
var count = 0
|
||||
while head.next != nil {
|
||||
count += 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
return count
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var peek: Element? { return head.next?.value }
|
||||
|
||||
func push(newElement: Element) -> Bool {
|
||||
let node = Node(value: newElement)
|
||||
node.next = head.next
|
||||
head.next = node
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func pop() -> Element? {
|
||||
let node = head.next
|
||||
head.next = node?.next
|
||||
return node?.value
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -6,9 +6,7 @@
|
||||
import Foundation
|
||||
|
||||
/// 用数组实现的队列
|
||||
struct ArrayQueue<T>: Queue {
|
||||
typealias Element = T
|
||||
|
||||
struct ArrayQueue<Element>: Queue {
|
||||
/// 数组
|
||||
private var items: [Element]
|
||||
/// 数组最大长度
|
||||
@ -78,9 +76,7 @@ struct ArrayQueue<T>: Queue {
|
||||
|
||||
/// 使用2个数组实现无界队列,用到 Swift 中 Array 较多的方法
|
||||
/// 来源:《iOS 面试之道》(故胤道长,唐巧)
|
||||
struct ArrayQueue2<T>: Queue {
|
||||
typealias Element = T
|
||||
|
||||
struct ArrayQueue2<Element>: Queue {
|
||||
/// 输入数组,主要负责入队
|
||||
var inArray = [Element]()
|
||||
/// 输出数组,主要负责出队
|
||||
|
||||
@ -6,9 +6,7 @@
|
||||
import Foundation
|
||||
|
||||
/// 循环队列
|
||||
struct CircularQueue<T>: Queue {
|
||||
typealias Element = T
|
||||
|
||||
struct CircularQueue<Element>: Queue {
|
||||
/// 数组
|
||||
private var items: [Element]
|
||||
/// 数组最大长度
|
||||
|
||||
@ -5,18 +5,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
import Foundation
|
||||
|
||||
class Node<T> {
|
||||
var value: T?
|
||||
var next: Node?
|
||||
|
||||
init(value: T) {
|
||||
self.value = value
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
struct QueueBasedOnLinkedList<T>: Queue {
|
||||
typealias Element = T
|
||||
|
||||
struct QueueBasedOnLinkedList<Element>: Queue {
|
||||
/// 队首
|
||||
var head: Node<Element>?
|
||||
/// 队尾
|
||||
@ -27,10 +16,15 @@ struct QueueBasedOnLinkedList<T>: Queue {
|
||||
var isEmpty: Bool { return head == nil }
|
||||
|
||||
var size: Int {
|
||||
var count = 0
|
||||
if isEmpty {
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var count = 1 // head 本身算一个
|
||||
while head?.next != nil {
|
||||
count += 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return count
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user